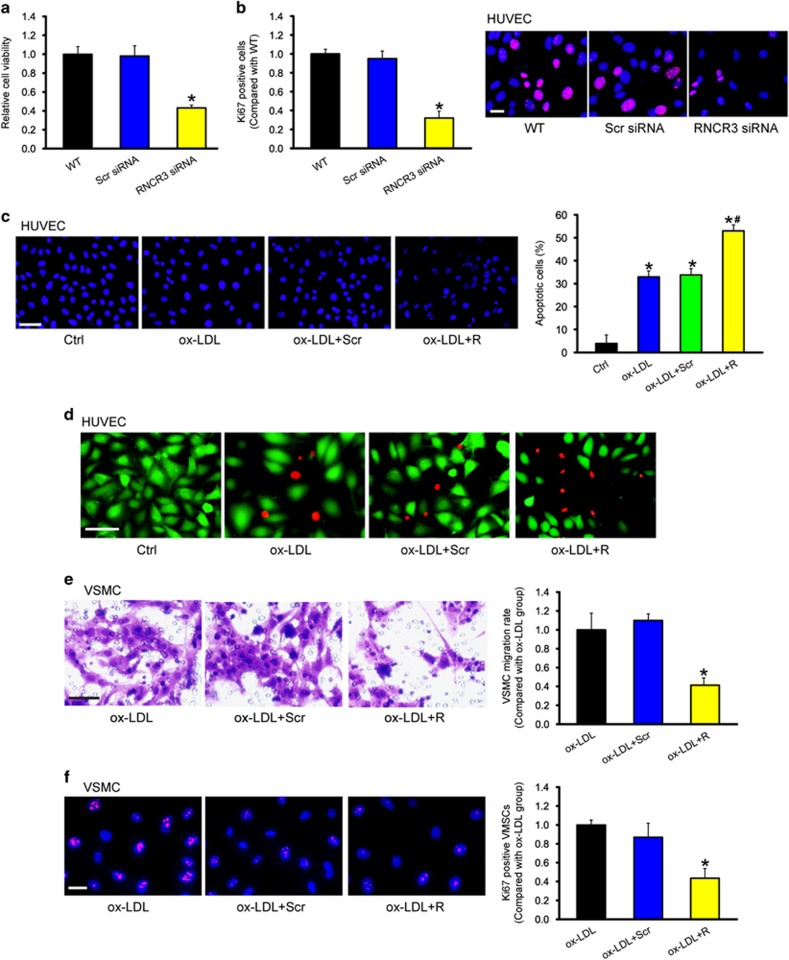
Figure 5.
RNCR3 knockdown affects EC and VSMC function in vitro. HUVECs were transfected with scrambled (Scr) siRNA, RNCR3 siRNA, or left untreated (WT) for 48 h. Cell viability was detected using MTT method. *P<0.05 versus WT group (a, n=4). Ki67 immunofluorescence staining and quantitative analysis showed that RNCR3 knockdown reduced HUVEC proliferation. Scale bar, 20 μm. *P<0.05 versus WT group (b, n=4). (c) HUVECs were transfected with scrambled (Scr) siRNA, RNCR3 siRNA, or left untreated (WT), and then exposed to ox-LDL (25 μg/ml) for 48 h. The group without ox-LDL treatment was taken as the control group (Ctrl). Apoptotic cells were analyzed using Hoechst staining and quantitated. Scale bar, 50 μm. *P<0.05 versus Ctrl group; #P<0.05 versus Ctrl group; #P<0.05 AS+Scr shRNA (Scr) versus AS+RNCR3 shRNA (R). Dead or dying cells were analyzed using calcein-AM/PI staining. Green, viable cells; red, dead or dying cell. Scale bar, 50 μm (d, n=4). (e, f) HUVECs were transfected with scrambled siRNA, RNCR3 siRNA, or left untreated, and then exposed to ox-LDL (25 μg/ml) for 48 h. The medium was collected from these experimental groups, and then co-cultured with VSMCs for 24 h. VSMC migration or proliferation was detected using transwell migration assay or Ki67 staining. A representative image of cell migration (e, scale bar, 50 μm, n=4) and cell proliferation (f, scale bar, 20 μm, n=4) and quantification results were shown. *P<0.05 versus ox-LDL group