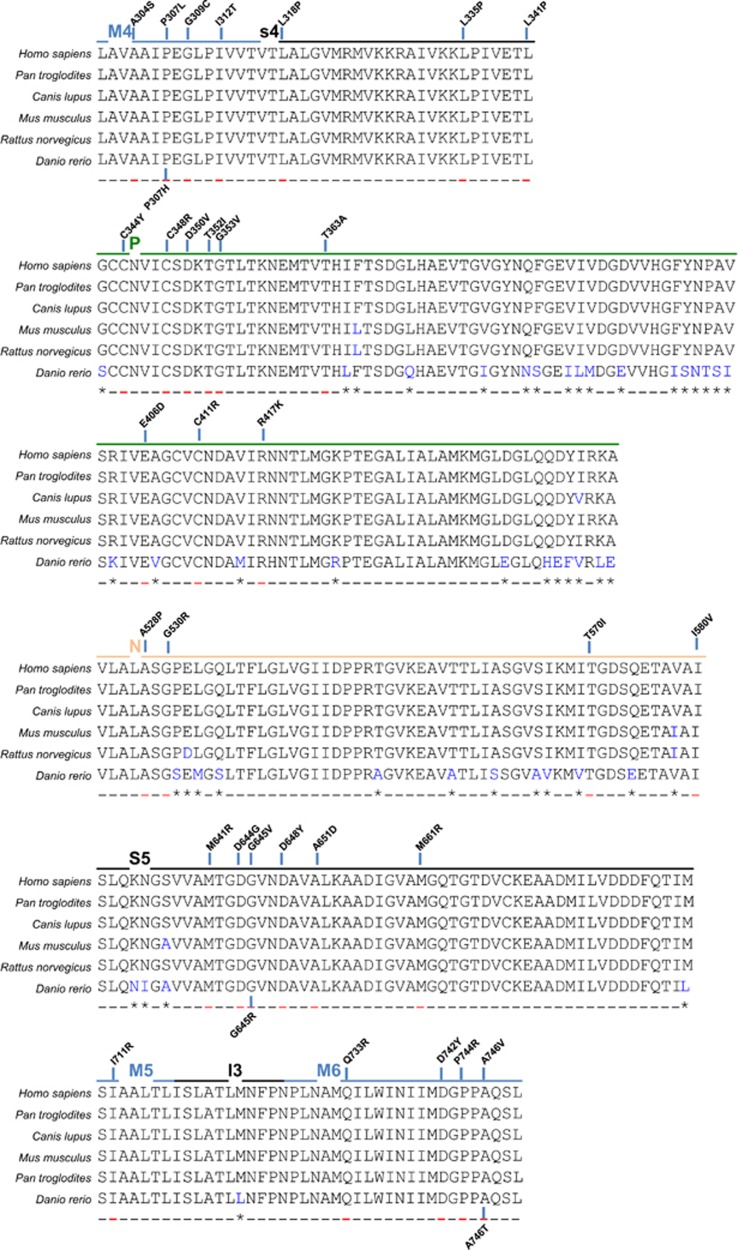
Figure 3.
Missense mutations mostly affect critical SPCA1 domains. Most of the missense mutations localize on exons 12, 13–16, 18, 21, and 23 of ATP2C1 gene coding for the indicated protein domains (M4, P, N, S5, M5-M6) crucial for the protein enzymatic activity and Ca2+/Mn2+ binding. In human HHD patients the missense mutations cause the indicated amino acid changes, supporting a crucial role for them in functionality of the SPCA1. Of note, the mutations localize on highly conserved residue/codon between the considered species, highlighting the importance of those encoded amino acids. In blue are indicated the different amino acids compared to the human sequence, in red where the mutations occur. Alignments were obtained from Ensembl database as described in Figure 1