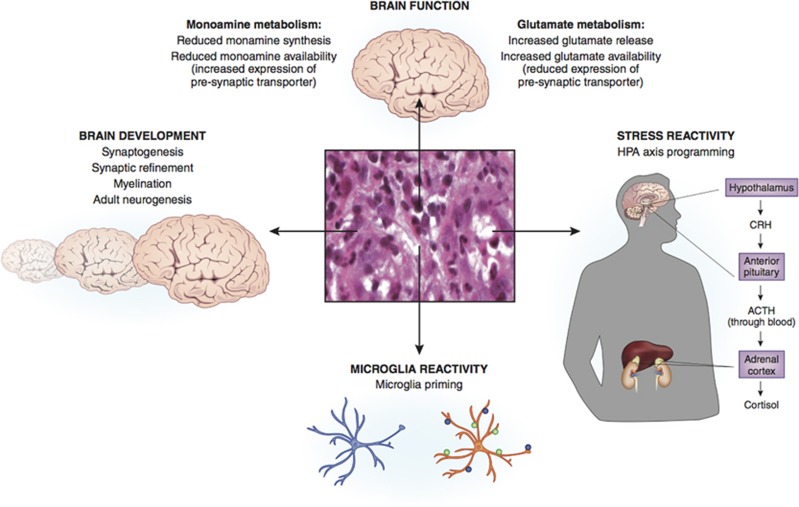
Figure 2.
Potential mechanisms linking childhood trauma-related inflammation to brain functioning and psychopathology. Mechanisms include the effects of inflammation on concurrent brain function, the effects of early immune activation on brain development, the sensitization of immune brain cells to subsequent psychosocial stressors, and the cross-sensitization of the HPA axis response to subsequent psychosocial stressors.