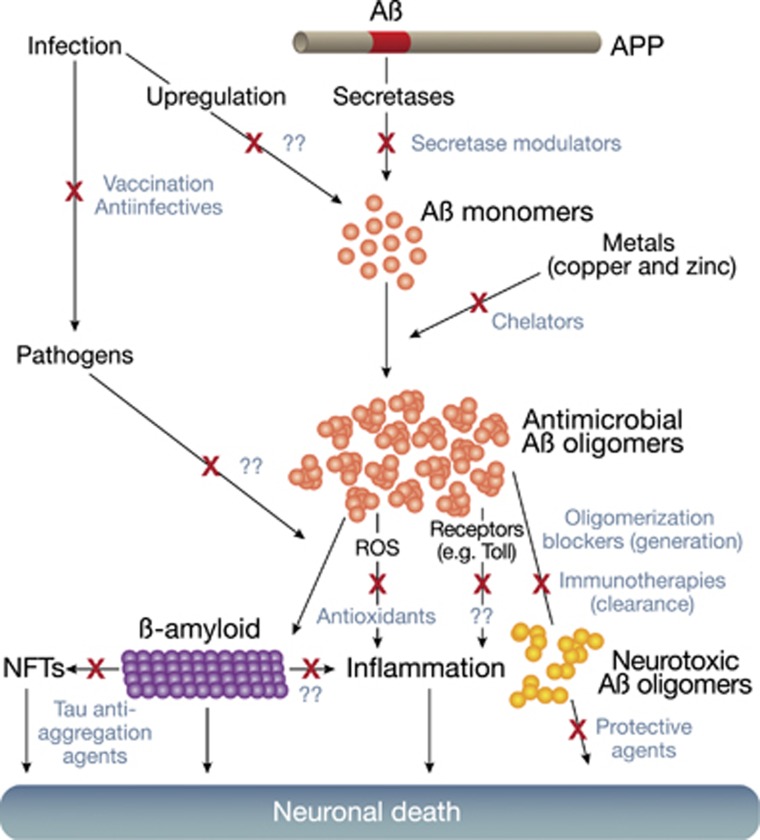
Figure 1.
Aβ oligomer pathways and potential targets for therapeutic intervention. Recent studies of ‘resilient' brains with high senile plaque loads have shown β-amyloid alone is insufficient for AD neurodegeneration. Neurofibrillary Tangles (NFTs) and neuroinflammation are also required. Shown are oligomer-mediated pathways contributing to neurodegeneration in AD and potential points for intervention (X). Possible approaches emerging from the antimicrobial peptide role of Aβ are indicated (??) as well as established therapeutic strategies, including secretase modulators that reduce the 42 amino acid Aβ isoforms (eg, GSM, NS-GSI, BSI), copper chelators (eg, PBT2), Aβ oligomerization blockers (eg, PBT2, ELND005, NRM8499), immunotherapies aimed at antibody-mediated clearance of Aβ (eg, Bapi, Sola), antioxidants that attenuate ROS-mediated inflammation (eg, vitamin E, epigallo-catechine gallate, resveratrol), agents purported to be neuroprotective (eg, dimebon), and drugs that inhibit tau aggregation and NTF generation (eg, rhodanine-based and Phenylthiazolyl-hydrazide inhibitors).