Figure 2.
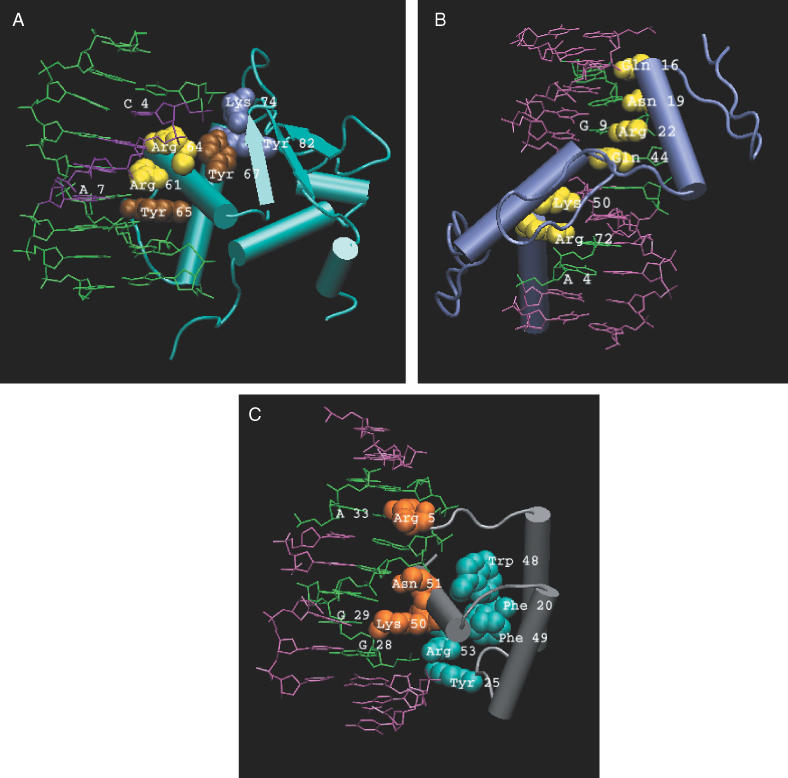
(A) Interface cluster (Type I) in SAP1 ETS transcription factor (1bc8C) of H.sapiens. The residues constituting the cluster are represented as vdw spheres. The sequence of DNA that directly interacts with the amino acids in the cluster is shown in purple. The residues Arg 61 and 64 interacting with DNA through cation–π interaction are shown in yellow, Tyr 65 and Tyr 67 in brown vdw spheres. Lys 74 and Tyr 82 are colored blue and are not involved in base recognition. Tyr 67 interacts with the backbone of DNA. The Figures 2 and 3 are prepared using VMD (28). (B) Interface clusters (Type II) in a synthetic zinc finger construct (1meyC). The residues Gln 16, Asn 19, Lys 22, Gln 44, Lys 50, Arg 72 are directly involved in base recognition and are represented as yellow vdw spheres. The bases of DNA that are specifically recognized by these residues are coloured green. (C) Interface and non-interface interactions in Engrailed Homeodomain of D.melanogaster (2hddA). The non-cluster-forming residues involved in specific base recognition are represented as orange vdw spheres. The cluster that is highly conserved and close to the interacting site is colored blue. Regions of DNA interacting with the proteins are colored green.
