Figure 1.
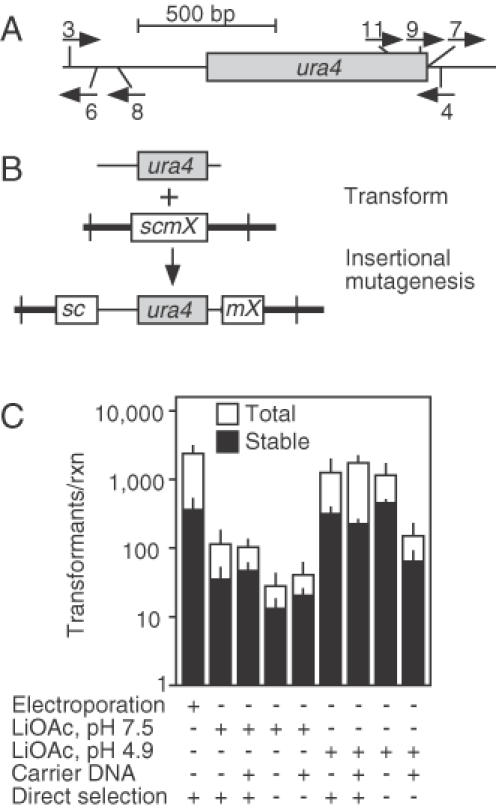
Insertional mutagenesis. (A) Schematic diagram of the ura4+ gene showing the coding region (box) and locations of the oligonucleotide primers (arrows). Oligonucleotide primers 3 and 4 were used to generate a 1.7 kbp long, linear ura4+ DNA fragment that was used for transformation. The other primers were used for subsequent analysis. (B) Transformation of a ura4-D18 (deletion) strain with linear ura4+ DNA leads to nonhomologous integration and insertional mutagenesis; stable Ura+ transformants can be screened for those which confer the desired mutant phenotype. (C) Effect of the transformation procedure on nonhomologous integration frequency. Shown are the total frequencies of Uracil prototrophic colonies (open bars) and the frequencies of stable transformants (filled bars). Data are mean ± standard deviation from three experiments.
