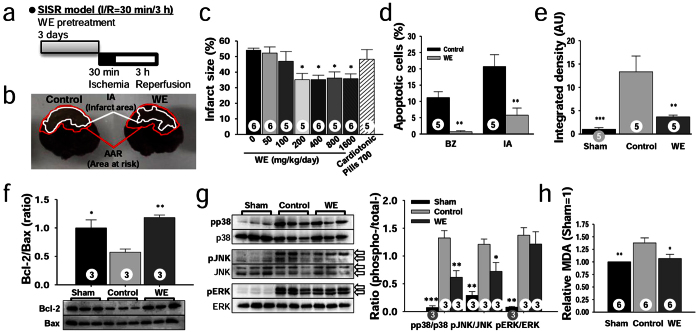
Figure 1. WE protects against myocardial injury from SISR by inhibiting apoptosis.
(a) Design of the SISR experiments. (b) Representative heart sections demarcating the area at risk (AAR) and infarct area (IA) for the control and WE-treated groups, respectively. (c) Effect of WE intake on infarct size (IS). (d) Ratio of apoptotic cells to total cells in the border zone (BZ) and IA as assessed by TUNEL and methyl green staining. (e) Relative levels of cleaved caspase-3 in the AAR assessed by immunohistochemical staining. AU, arbitrary unit. (f) Bcl-2 and Bax levels presented as the Bcl-2/Bax ratio in the AAR, measured by Western blotting. (g) Phosphorylated p38, JNK, and ERK levels in the AAR as measured by Western blotting (left) and pMAPK/total MAPK ratios (right). The original bands are presented in Supplementary Fig. S2. (h) Relative malondialdehyde (MDA) levels in the AAR analysed through a chromogenic assay. In panels (d–h), WE was supplemented at a dose of 400 mg/kg/day. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with the controls. The numbers inside the bars indicate the number of animals per group.