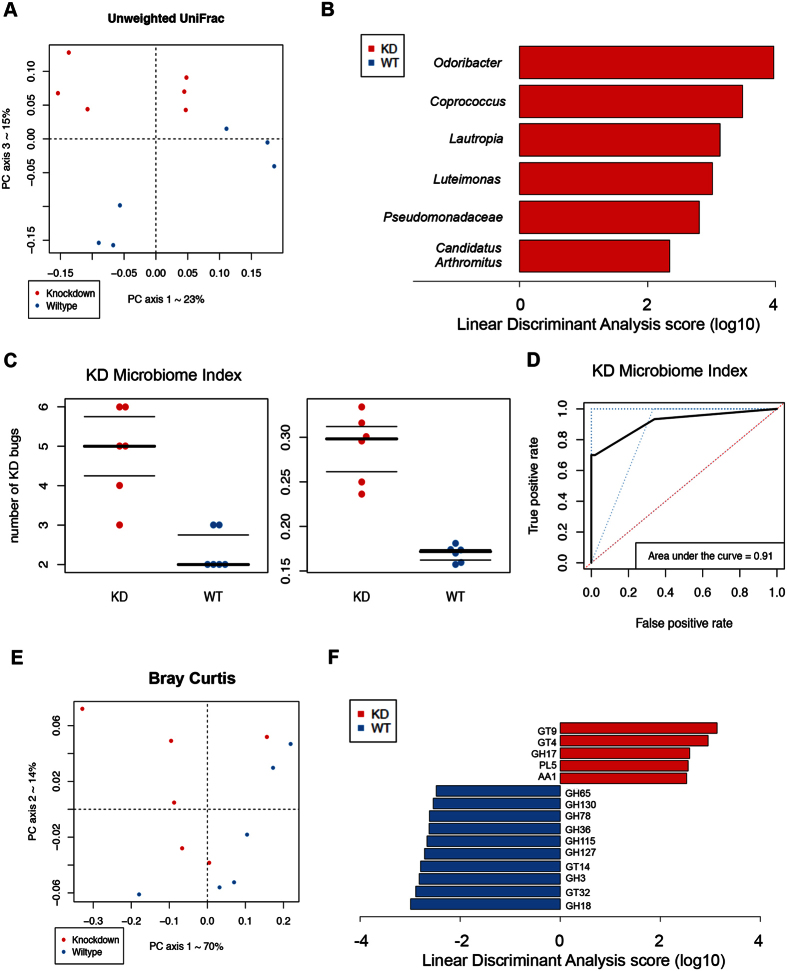
Figure 1. Macrophage RIP140 level alters the composition and functional repertoire of intestinal microbiota.
(A) Beta diversity comparisons of the gut microbiomes of the fecal samples collected from WT and RIP140mϕKD mice receiving High Fat Diet. Analyses were performed on 16 S rRNA V4 regions data with a rarefaction depth of 66677 reads per sample. Principal coordinates analysis of Unweighted UniFrac distances. Proportion of variance explained by each principal coordinate axis is denoted in the corresponding axis label. The plot shows a separation between samples from WT and RIP140mϕKD mice receiving High Fat Diet (PERMANOVA, p = 0.04). (B) Summary of the taxa that differentiate WT from RIP140mϕKD mice receiving HFD using Linear discriminant analysis Effect Size analysis (LEfSe). (C) Left: KD microbiome index corresponding to the sum of number of genera among the differentiating taxa. Data were presented with Mann–Whitney U test: p-value = 0.007. Right: KD microbiome index corresponding to the total relative abundance of the differentiating taxa. Data were presented with Mann–Whitney U test: p-value = 0.002. (D) ROC curve analysis for KD microbiome index. (E) Beta-diversity plots from Bray-Curtis distance matrices for genome analysis. (F) CAZY GH assignments for glycoside hydrolase families analysis.