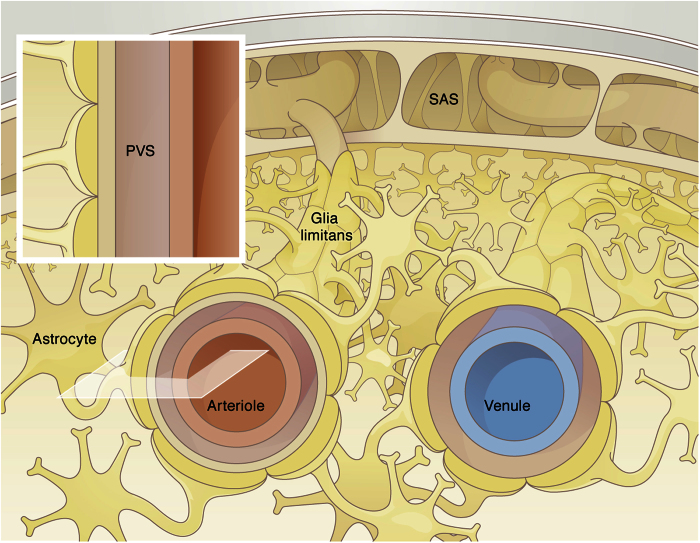
Figure 2. Schematic of cerebral arterial and venous paravascular spaces.
The arterial PVS extends from the subarachnoid space (SAS) and follows the penetrating vessel into the tissue. This space is restricted on the one side by the vascular wall (endothelial and smooth muscle cells) and on the other side by the glia limitans. Glial endfeet processes almost completely cover the PVS of the larger vessels. The glia limitans of the arterial PVS is attached to the pia matter that extends from the SAS into the parenchyma. The inset shows the section of the arterial PVS retained for the axisymmetric computational model domain.