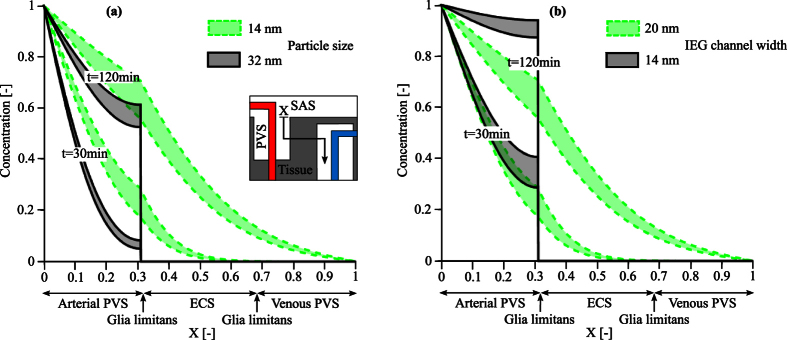
Figure 6.
Spatial and temporal distribution of the solute concentrations in the brain (a) for two different particle sizes, 14 and 32 nm, respectively, assuming an IEG width of 20 nm (b) and for the 14 nm particle under the effect of IEG width reduction from 20 nm to 14 nm. Results represent a range of plausible dispersion coefficients as reported in Table 2. In both cases, the particles enter the arterial PVS from the arterial PVS-SAS interface. While in the normal glia limitans morphology (a) the larger particles (32 nm in size) are already trapped by this layer and cannot pass into the parenchyma, reduction of IEG width (b) also inhibits passage of the smaller solute.