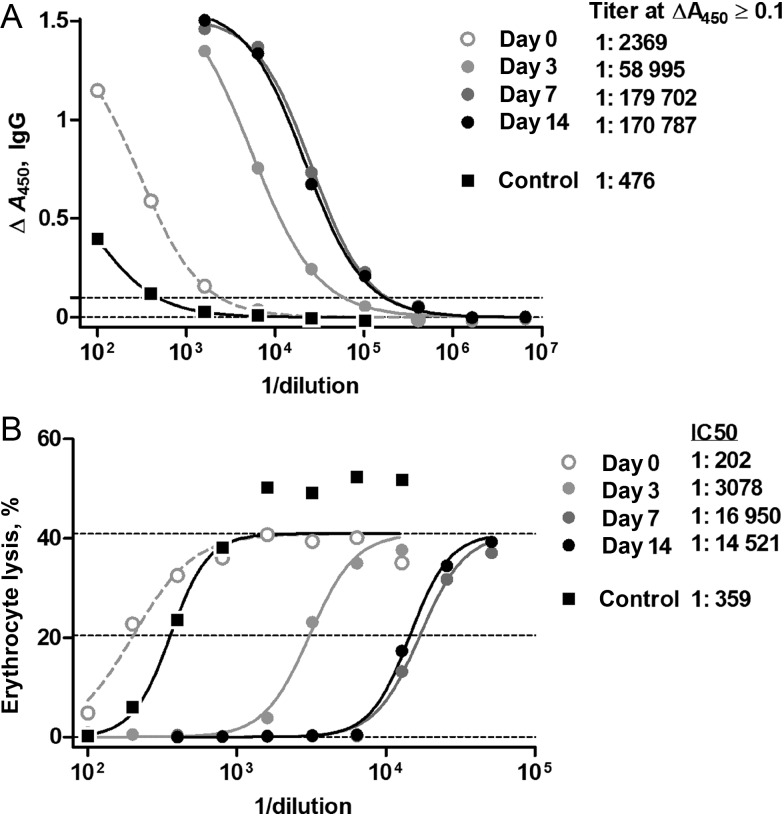
Figure 1.
α-Toxin–specific antibody measurements on a representative patient coinfected with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and influenza virus. Four serial serum samples from 1 MRSA-coinfected patient, a 2.7-year-old male presenting with shock and acute lung injury, were subjected to the assays as described in “Methods” section; a healthy adult donor control serum is included. A, α-Toxin–binding antibody as measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), using an immunoglobulin G (IgG)–specific secondary detector. The x-axis denotes the reciprocal dilution of patient serum. The dotted line denotes the threshold for computation of the end point titer, arbitrarily defined at 0.1 specific absorbance units. B, Residual hemolytic activity of 2 nM recombinant α-toxin incubated with serial dilutions of patient serum. Lines denote minimum, maximum, and half-maximum hemolytic activities. The computed titers and inhibitory concentration for half-inhibition (IC50) levels are as listed.