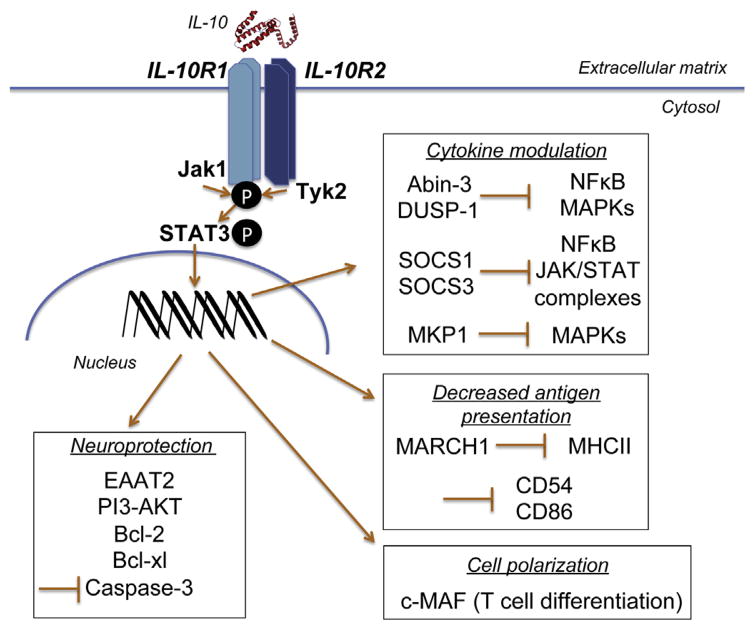
Fig. 2.
Interleukin-10 (IL-10) receptor signaling. IL-10 exerts effects through a heterotetramer consisting of two IL-10 receptor 1 (IL-10R1) chains and two IL-10 receptor 2 (IL-10R2) chains. IL-10R1 activates Janus kinase 1 (Jak1), while IL-10R2 activates tyrosine kinase 2 (Tyk2), leading to phosphorylation of IL-10R1 followed by phosphorylation of STAT3 (other STAT proteins have also been implicated including STAT4 in TH1 cells; STAT6 and GATA3 in TH2 cells; and, STAT1 and STAT3 in TH17 cells). Such signaling results in diverse consequences, such as a) cytokine modulation by the induction of A20-binding inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NFκB) (Abin-3) and dual specificity phosphatase-1 (DUSP-1) that inhibit mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphorylation as well as NFkB. Suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) 1 and 3 are also produced which target the p65 NFκB subunit for degradation and mark activated JAK-STAT complexes for degradation. Mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphatase (MKP) expression, including MKP1, is elevated to inhibit MAPK signaling; b) decreased antigen presentation by reducing expression of major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC II) molecules by inducing membrane-associated RING-CH (MARCH) 1 and by inhibiting expression of adhesion (e.g. CD54) and co-stimulatory (e.g. CD86) molecules c) cell polarization via induction of transcription factors such as c-MAF, and d) neuroprotection by normalizing expression of excitatory amino acid transporter-2 (EAAT2), by releasing intracellular calcium stores via PI3K-AKT, by preventing apoptosis through restoration of suppressed anti-apoptotic factors Bcl-2 and Bcl-xl, and by attenuating caspase-3 expression.