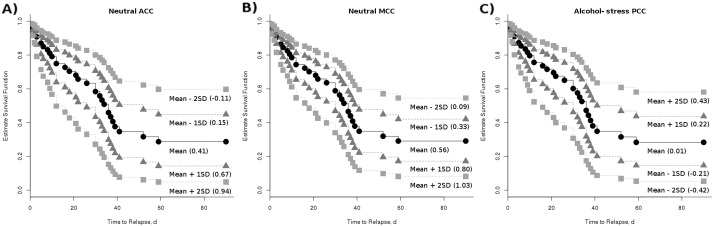
Fig. 2.
Estimated survival functions for connectivity predicting relapse. Estimated survival functions for time to relapse (with the number of years of alcohol use and nicotine smoking held constant) are shown for the mean ICD connectivity value and ± 1 and 2 standard deviation above/below the mean. Weaker connectivity in the A) ACC and B) MCC during neutral cueing was significantly (p < 0.05) associated with longer time to relapse. C) Greater connectivity in the PCC during alcohol cueing compared to stress cueing was significantly (p < 0.05) associated with longer time to relapse. These figures of estimated survival functions show the x-axis up to day 60 because all patients who relapsed in the 90-day follow-up period relapsed with-in 60 days.