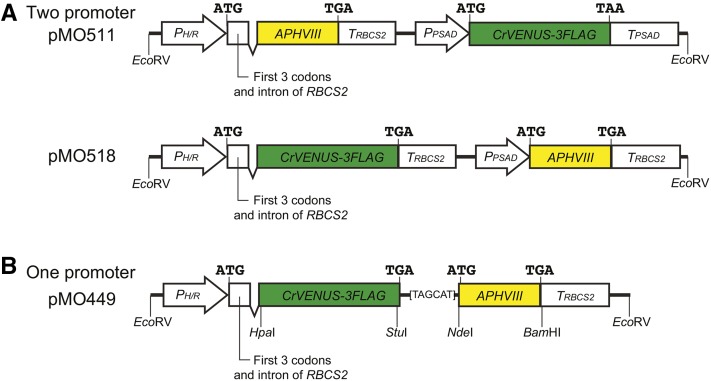
Figure 1.
Representative two-promoter and one-promoter expression constructs as used in this study. All constructs were embedded in the identical plasmid backbone (outside of the EcoRV sites shown), as described in Materials and Methods. (A) Two-promoter constructs. Translation start and stop sites for each gene are shown. PH/R, strong hybrid HSP70A/RBCS2 promoter; APHVIII, paromomycin-resistance gene; TRBCS2, RBCS2 transcription terminator; PPSAD, strong PSAD promoter; CrVENUS-3FLAG, coding sequence of Venus codon-optimized for Chlamydomonas and tagged with three copies of the FLAG epitope; TPSAD, PSAD transcription terminator; EcoRV, restriction sites that can be used to excise the construct from the vector before transformation. Other restriction sites are present [cf. (B)] but not shown. (B) General structure of the one-promoter constructs used in this study as illustrated by that of plasmid pMO449. The 6-bp linker between the two ORFs is shown by the sequence of the transcribed strand; other symbols as in (A). The restriction sites shown can be used to replace the upstream GOI, the downstream selectable marker, or the linker sequence (see text).