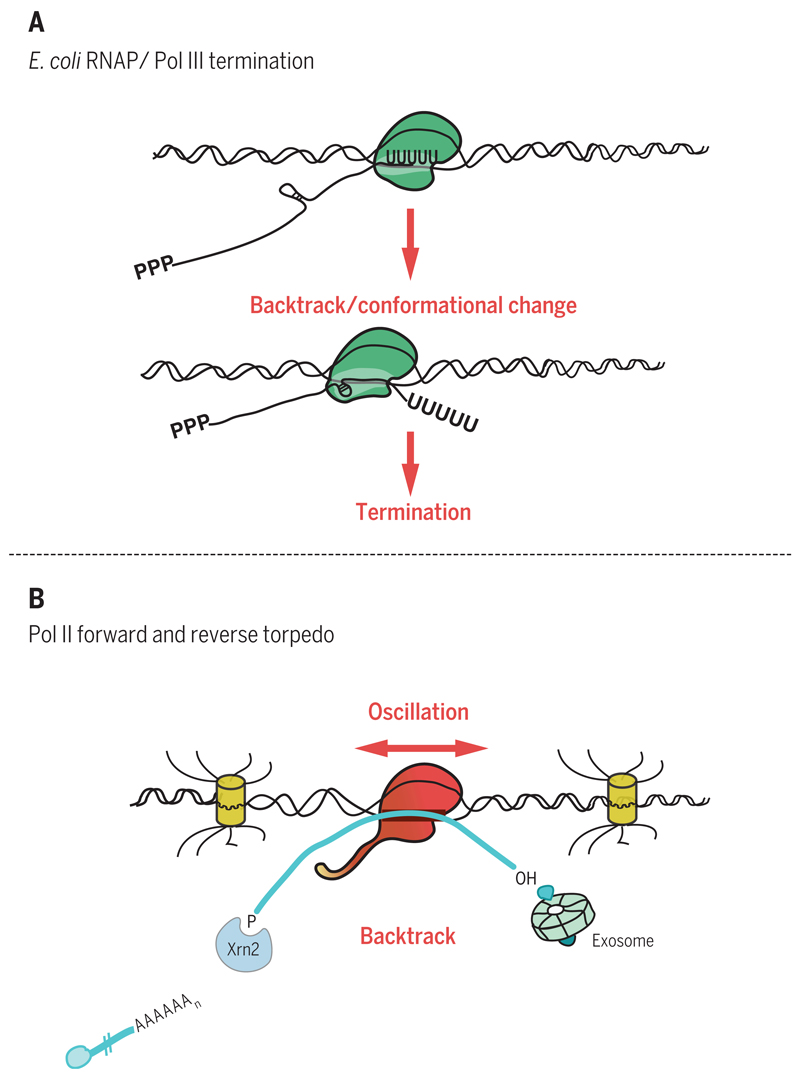
Fig. 2. Pol II backtracking.
(A) Bacterial RNA polymerase or Pol III terminates at an oligo(U) transcript, which pauses polymerase and promotes backtracking. An upstream RNA hairpin is forced into polymerase active site, inducing a conformational change that results in termination. (B) Pol II moves forward to synthesize or backward to extrude transcript (oscillation). Forward transcript, once cleaved at PAS to release mRNA, is then degraded by Xrn2. Backtracked transcript is degraded by the exosome. Removal of RNA up to Pol II (forward or reverse torpedo) induces termination.