Figure 3.
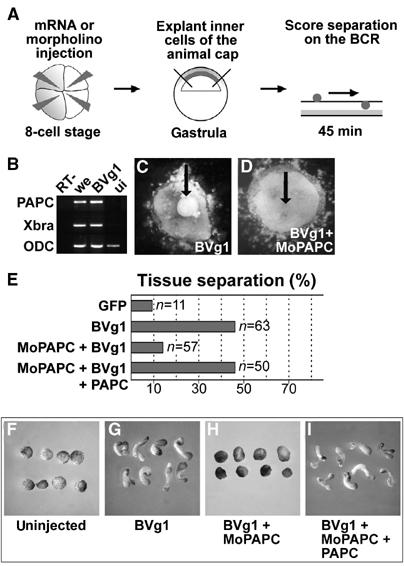
PAPC function is necessary for BVg1-induced separation behavior and elongation of animal caps. (A) Scheme describing the blastocoel roof assay for analysis of separation behavior. (B) RT–PCR analysis of Xbra and PAPC expression in BVg1 mRNA (50 pg)-injected animal caps. (C) BVg1-injected animal cap cells show separation behavior. (D) Coinjection of 80 ng MoPAPC abolishes BVg1-induced separation behavior. (E) Compilation of the in vitro separation assays. (F–I) BVg1-induced elongation of animal caps requires PAPC function. (G) Injection of 50 pg of BVg1 mRNA induces elongation of animal caps. (H) MoPAPC (80 ng) injection abolishes BVg1-induced elongation of animal caps. (I) Injection of 800 pg of mRNA for PAPC rescues the effect of MoPAPC.
