Figure 5.
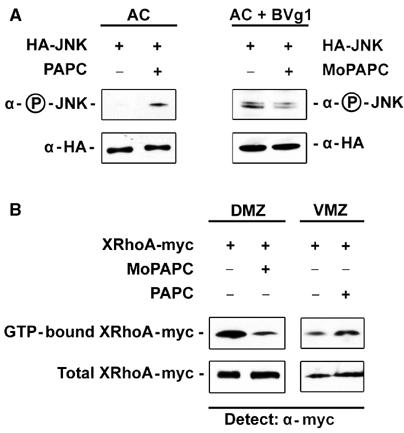
PAPC activates JNK and RhoA. For the JNK activity assay, 200 pg of HA epitope-tagged JNK mRNA was injected either alone or in combination with 500 pg of PAPC mRNA into the animal blastomeres at the four-cell stage. HA-JNK was precipitated from extracts of 20 embryos at stage 11 and activation of JNK was monitored by its phosphorylation using a phosphospecific antibody. (A) JNK is activated by PAPC mRNA expression as measured by JNK phosphorylation. Equal amounts of immunoprecipitated HA-JNK were loaded in each lane. Injection of 100 pg of BVg1 mRNA activates JNK and injection of MoPAPC inhibits BVg1-induced activation of JNK. (B) PAPC expression enhances RhoA activity in the VMZ and PAPC function is required for RhoA activity in the DMZ. For gain of PAPC function assays, myc epitope-tagged RhoA DNA was injected into the VMZ either alone or in combination with 1 ng of PAPC mRNA. Activated RhoA was precipitated from 30 early gastrulae by RBD-GST, blotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane and detected using anti-myc Ab1 monoclonal antibody. Whole embryo extract was used as a loading control. Overexpression of PAPC causes activation of RhoA in the VMZ as monitored by precipitation of active RhoA by RBD-GST. Loss of PAPC function by MoPAPC (80 ng) injection greatly reduced RhoA activity in the DMZ.
