Figure 3.
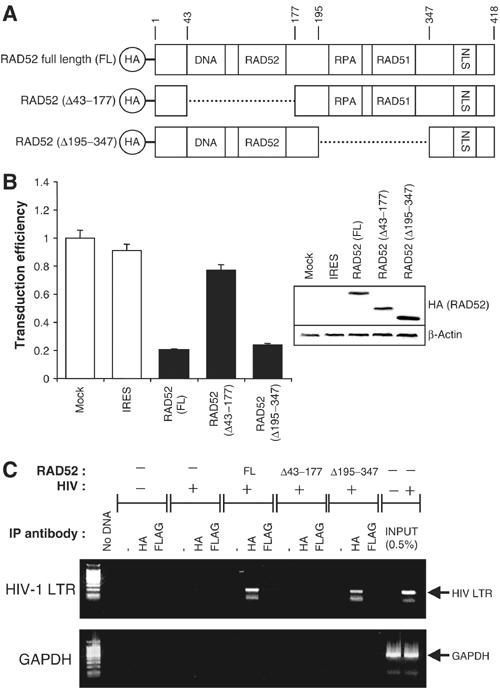
The DNA-binding domain of RAD52 is required for inhibition of retroviral infection. (A) Schematic of HA-tagged RAD52 and deletion mutants showing functional domains (DNA: DNA-binding domain; RAD52: RAD52 self-association domain; RPA: RPA-binding domain; RAD51: RAD51-binding domain; NLS: nuclear localisation signal, with amino-acid residues numbered). (B) 293 cells transiently transfected with full-length (FL) RAD52 and RAD52 deletion mutant expression plasmids subsequently infected with HIV-1 luciferase retroviral stocks. HIV-1 luciferase transduction results (left) and immunoblot analysis of cell lysates (right) are shown. Results are expressed as luciferase activity relative to untransfected 293 cells. Immunoblots were performed using anti-HA tag antibodies before re-probing for β-actin (loading control). (C) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis of 293 cells transiently transfected with FL-RAD52 or RAD52 deletion mutant expression plasmids and infected with HIV-1 luciferase retroviral stocks. Levels of HIV-1 DNA physically associated with HA-RAD52 were determined by immunoprecipitation with anti-HA antibodies and PCR performed using primers against HIV-1 LTR sequences (upper panel) or genomic GAPDH sequences (lower panel). Nonspecific control immunoprecipitations were performed using either no antibody (−) or an IgG1 isotype control anti-FLAG tag antibody. For reference, 0.5% of the total amount of HIV-1 LTR DNA formed during a typical infection is also shown (INPUT).
