Figure 8.
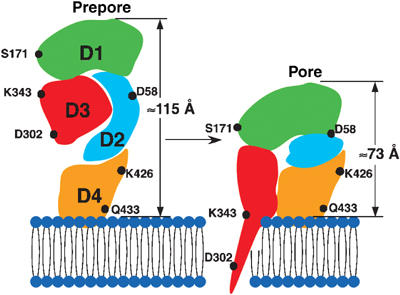
Schematic structural model of the prepore-to-pore transition of PFO. The data presented here suggest that the conformation of PFO in the prepore complex is largely the same as that of the water-soluble monomer, attached to the membrane in a perpendicular orientation via the tip of its domain 4. At the prepore stage of formation, the TMHs are ∼40 Å from the membrane surface. Upon converting to the pore, there is a vertical collapse of the structure by 40 Å, which changes neither the outer diameter of the complex nor the structure of its topmost surface significantly. We propose that the vertical collapse is a consequence of a disruption of the extended domain 2 structure. As a result of this collapse, the TMHs are brought close enough to the membrane surface to be able to span the bilayer and line the pore.
