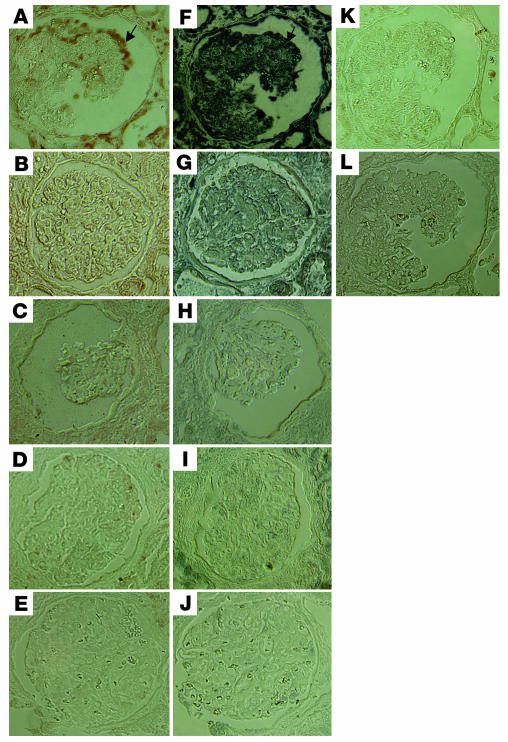
Figure 9.
Immunohistochemistry of signaling molecules in kidney biopsies. Immunostaining of phospho-Stat3 and phospho-MAPK1,2 was performed in kidney biopsies from HIVAN patients and compared with that in kidney biopsies from HIV patients with non-HIVAN kidney diseases or from non-HIV patients with idiopathic collapsing FSGS, classic FSGS, or minimal-change disease. Representative pictures are shown. (A) Phospho-MAPK1,2 in HIVAN kidney. (B) Phospho-MAPK1,2 in non-HIVAN kidney (hypertension). (C) Phospho-MAPK1,2 in idiopathic collapsing FSGS kidney (in a patient with negative staining). (D) Phospho-MAPK1,2 in classic FSGS kidney. (E) Phospho-MAPK1,2 in minimal-change disease kidney. (F) Phospho-Stat3 in HIVAN kidney. (G) Phospho-Stat3 in non-HIVAN kidney. (H) Phospho-Stat3 in idiopathic collapsing FSGS kidney (in a patient with negative staining). (I) Phospho-Stat3 in classic FSGS kidney. (J) Phospho-Stat3 in minimal-change disease kidney. (K) Negative control for phospsho-MAPK1,2. (L) Negative control for phospho-Stat3. ×400. Arrows in A and F indicate colocalization of phospho-MAPK1,2 and phospho-Stat3.