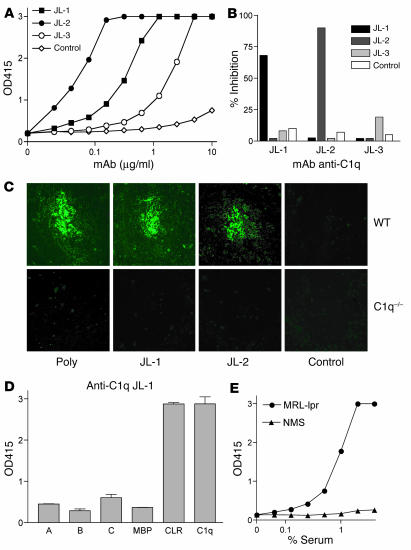
Figure 1.
In vitro characterization of mouse anti–mouse C1q mAb. (A) Anti-C1q detection ELISA for anti-C1q mAb’s JL-1, JL-2, and JL-3 and control mAb IgG2b under 0.5 M NaCl buffer conditions. OD415, OD at 415 nm. (B) Epitope competition ELISA showing inhibition of binding of DIG-labeled anti-C1q mAb to mouse C1q by unlabeled anti-C1q mAb or control mAb IgG2b. (C) Immunohistochemistry of WT or C1q–/– mouse spleen stained with anti-C1q mAb or controls. Original magnification, ×250. Poly, polyclonal antibody. (D) C1q head domains of the human A, B, and C chains or the control maltose-binding protein (MBP), CLRs, and intact human C1q were coated, and mAb JL-1 binding was analyzed. (E) Anti-C1q tail ELISA using human CLRs and serum of autoimmune MRL-lpr mice (MRL-lpr) or nonautoimmune normal mouse serum (NMS) for binding.