Figure 5.
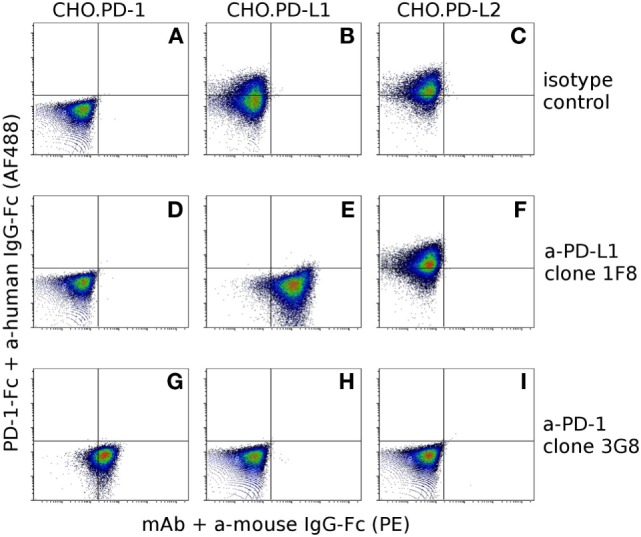
Confirmation of antibody specificity and blocking capacity. To assess the specificity and blocking capacity of devil-specific α-PD-L1 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) CHO.PD-1 (A,D,G), CHO.PD-L1 (B,E,H), and CHO.PD-L2 (C,F,I) transfected cells were preincubated with α-PD-L1 mAb clone 1F8 or isotype control antibodies prior to incubation with recombinant PD-1 fused to human IgG1-Fc (PD-1-Fc). Cells were then incubated with secondary anti-human IgG-Fc AlexaFluor 488 and anti-mouse IgG-phycoerythrin to detect PD-1-Fc binding and α-PD-L1 binding. Cells in the upper left quadrant indicate PD-1-Fc binding to the cell line and cells in the lower right indicate binding of mAbs to the cell line. Graphs (A–F) show that α-PD-L1 clone 1F8 binds to PD-L1, but not to PD-1 or PD-L2 and that clone 1F8 blocks binding of PD-1-Fc to PD-L1 but not to PD-L2. In order to asses blocking capacity of α-PD-1 mAbs, PD-1-Fc was preincubated with α-PD-1 mAb 3G8 prior to incubation with CHO.PD-1 (G), CHO.PD-L1 (H), or CHO-PD-L2 (I). Graphs (G–I) show that α-PD-1 clone 3G8 is specific for PD-1 and blocks binding of PD-1-Fc to both PD-L1 and PD-L2.
