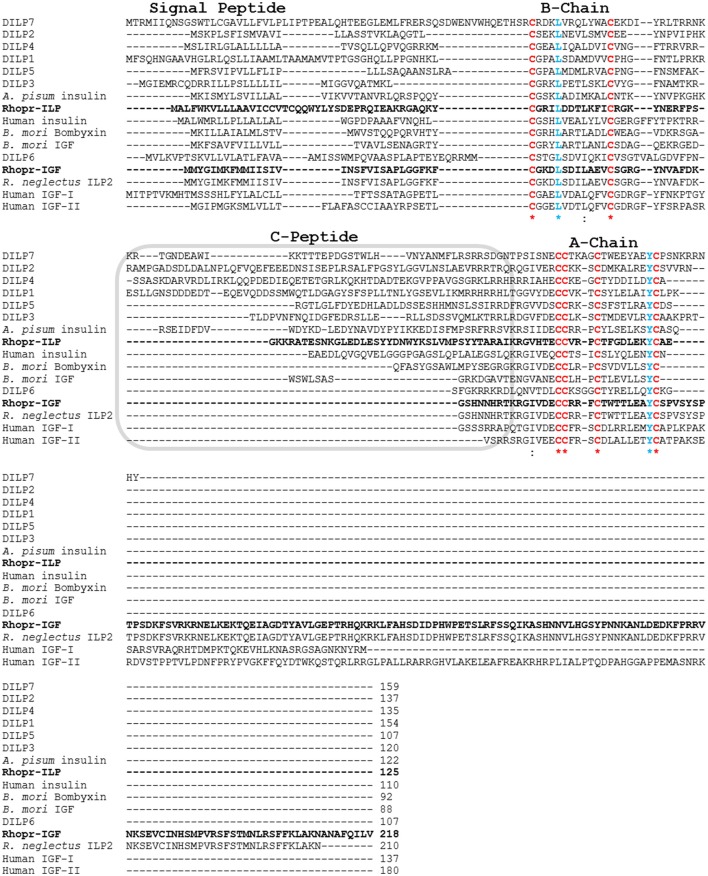
Figure 2.
Multiple sequence alignment of prepropeptides of insect ILPs and IGFs and human insulin and IGFs. Rhop-IGF (KX185519) and Rhopr-ILP (KT896507) are highlighted in bold and were aligned with 11 ILPs from other insect species (D. melanogaster DILP1 NP_648359.1, D. melanogaster DILP2 NP_524012.1, D. melanogaster DILP3 NP_648360.2, D. melanogaster DILP4 NP_648361.1, D. melanogaster DILP5 NP_996037.1, D. melanogaster DILP6 NP_570000.1, D. melanogaster DILP7 NP_570070.1, Acyrthosiphon pisum insulin XP_001949438.1, B. mori bombyxin BAA00246.1, B. mori IGF NP_001138796.1, R. neglectus ILP2 A0A0N7Z9F4), and with human insulin and IGFs I/II (human insulin CAA23828.1, human IGF-I NP_001104754.1, human IGF-II NP_001007140.2). Chains A and B and the C-peptide region are indicated. The six conserved cysteines that form the three disulfide bonds in the mature peptides are highlighted in red, while the other highly conserved residues are highlighted in blue (L and Y), emphasized by *indicates conservation between groups of strongly similar amino acids.