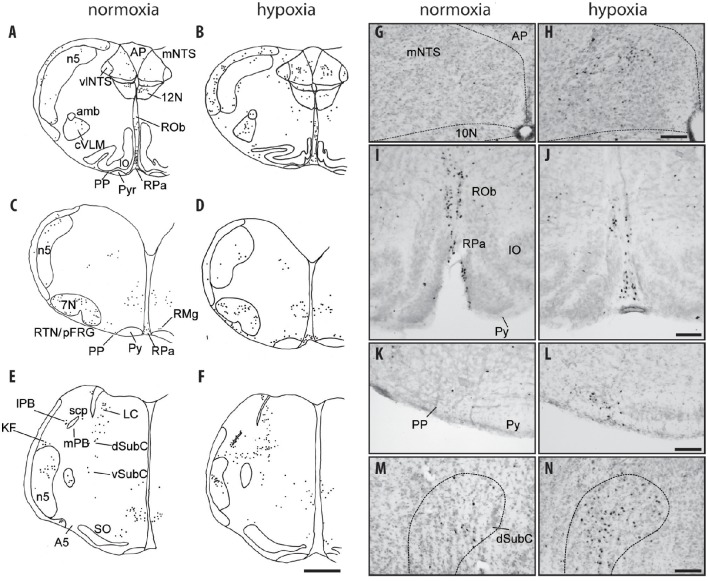
Figure 2.
c-FOS-positive cells in the medulla oblongata and pons of one-day-old mice under hypoxia. Drawings of representative sections from the medulla oblongata (A–D) and pons (E,F) under normoxia (A,C,E) and hypoxia (B,D,F). Scale bar = 500 μm. Photomicrographs of c-FOS immunoreactivity in the mNTS (G,H), the RPa and ROb (I,J), the PP (K,L), and the dSubC (M,N) under normoxia (G,I,K,M) and hypoxia (H,J,L,N). Scale bar = 100 μm. 7N, facial nucleus; 10N, dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus 12N, hypoglossal nucleus; A5, A5 region; Amb: ambiguus nucleus; AP, area postrema; dSubC, dorsal part of the subcoeruleus nucleus; mNTS, median part of the nucleus of the tractus solitarius; cVLM, caudal part of the ventrolateral medullary reticular nucleus; PP, parapyramidal group; Py, pyramidal tract; RPa, raphe pallidus nucleus; RMg, raphe magnus nucleus; RTN/pFRG, retrotrapezoid nucleus/parafacial respiratory group; vlNTS, ventrolateral part of the nucleus of the tractus solitarius; vSubC, ventral part of the subcoeruleus nucleus.