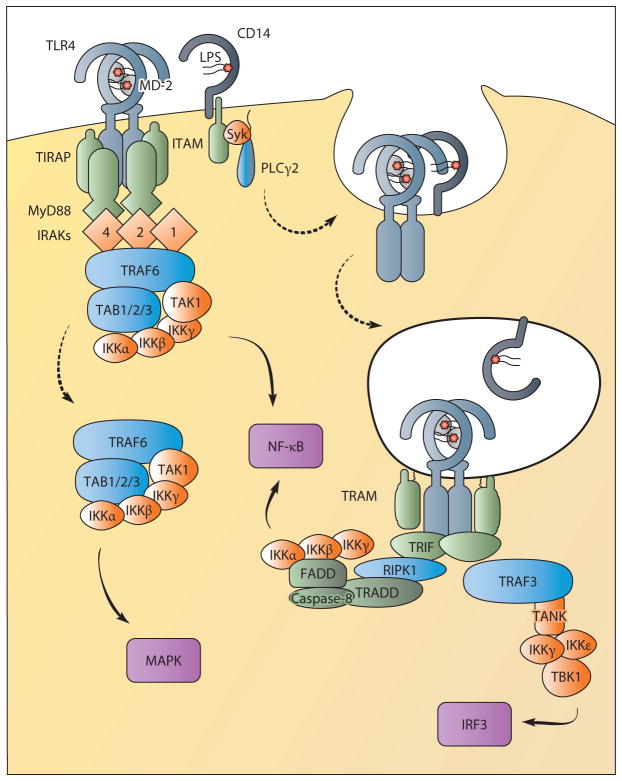
Figure 2.
TLR4 signals from the plasma membrane and endosomes. TLR4 requires translocation to lipid rafts enriched with TIRAP for signaling from the plasma membrane. This facilitates interactions with MyD88 upon ligand binding for the formation of the myddosome containing MyD88, TIRAP, and IRAKs. The IRAKs recruit the E3 ubiquitin ligase TRAF6, which interacts with a complex formed by TAB1, TAB2, TAB3, and TAK1. This complex regulates NF-κB activation via IKKs. TAK1 release into the cytoplasm also directs MAPK activation. CD14 controls the movement of TLR4 from the plasma membrane into endosomes through the activation of ITAM, Syk, and PLCγ2. From endosomes, TLR4 interacts with the sorting adaptor TRAM and the signaling adaptor TRIF to sustain NF-κB activation and to induce IRF3-mediated type I IFN production. TRIF-dependent NF-κB activation may proceed via the proteins RIPK1, TRADD, and the caspase-8 complex. IRF3 activation controls type I IFN production and requires TRAF3 recruitment to TRIF. TRAF3 then interacts with TANK (or TANK-related proteins) to recruit IKKγ, IKKε, and TBK1, which activate IRF3. (Solid lines indicate signal transduction; dotted lines indicate trafficking events.) (Abbreviations: FADD, Fas-associated protein with death domain; IKK, IκB kinase; IRAK, interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase; IRF, IFN regulatory factor; ITAM, immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; PLCγ2, phospholipase Cγ2; RIPK1, receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1; TAB, TAK1-binding protein; TAK, TGF-β-activated kinase; TANK, TRAF family member–associated NF-κB activator; TBK, TANK-binding kinase; TIRAP, TIR-containing adaptor protein; TRADD, TNF receptor type 1–associated death domain; TRAF, TNF receptor–associated factor.)