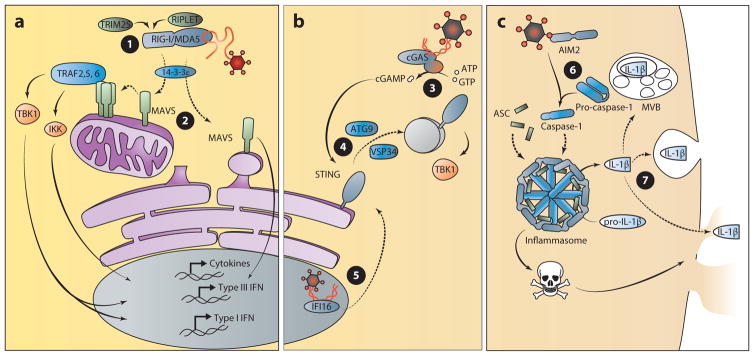
Figure 5.
The biosynthetic pathway: nucleic acid detection from within the cytosol. (a) The RLRs detect pathogen-derived RNA within the cytosol to induce the production of IFN and proinflammatory cytokines. The TBK1, IKK, and MAVS pathways lead to activation of the transcription factors for the induction of IFN and other cytokine genes. ➊ RIG-I signal transduction is regulated by TRIM25- and RIPLET-mediated ubiquitination and translocation to the site of signaling by 14-3-3ε. ➋ MAVS activity is regulated by polymerization, and signaling from mitochondria results in production of type I and III IFN, whereas peroxisomal signaling induces the production only of type III IFN. (b) cGAS and the ALRs detect pathogen-derived DNA from within the cytosol and nucleus to induce the production of IFN. ➌ In the presence of DNA, the enzyme cGAS converts ATP and GTP to the cyclic dinucleotide cGAMP. ➍ Production of cGAMP induces the activation and trafficking of STING to poorly defined sites of signaling in an ATG9- and VSP34-dependent manner. TBK1 is recruited to this site of signaling to induce the production of type I IFN. ➎ Viral DNA within the nucleus can be detected by IFI16 for the production of type I IFN in a STING-dependent manner. Therefore, the trafficking of this receptor or another factor from the nucleus to the cytosol may regulate IFI16-dependent signaling. (c) The inflammasome-mediated response to DNA within the cytosol. ➏ AIM2 detection of cytosolic DNA activates inflammasome formation, which induces cell death and the maturation of IL-1β. ➐ Secretion of this cytokine requires a noncanonical route that is independent of trafficking through the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. Several possibilities have been proposed for IL-1β release that include routes through lysosomal compartments, multivesicular bodies, or pores created during pyroptotic cell death. (Solid lines indicate signal transduction; dotted lines indicate trafficking events.) (Abbreviations: AIM, absent in melanoma; cGAMP, cyclic di-GMP/AMP; cGAS, cyclic GMP-AMP synthase; IFI, interferon, γ-inducible; IFN, interferon; IKK, IκB kinase; MAVS, mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein; MDA, melanoma differentiation gene; RIG-I, retinoic acid–inducible gene I; STING, stimulator of IFN gene; TBK, TANK-binding kinase; TRAF, TNF receptor–associated factor; TRIM25, tripartite motif-containing 25.)