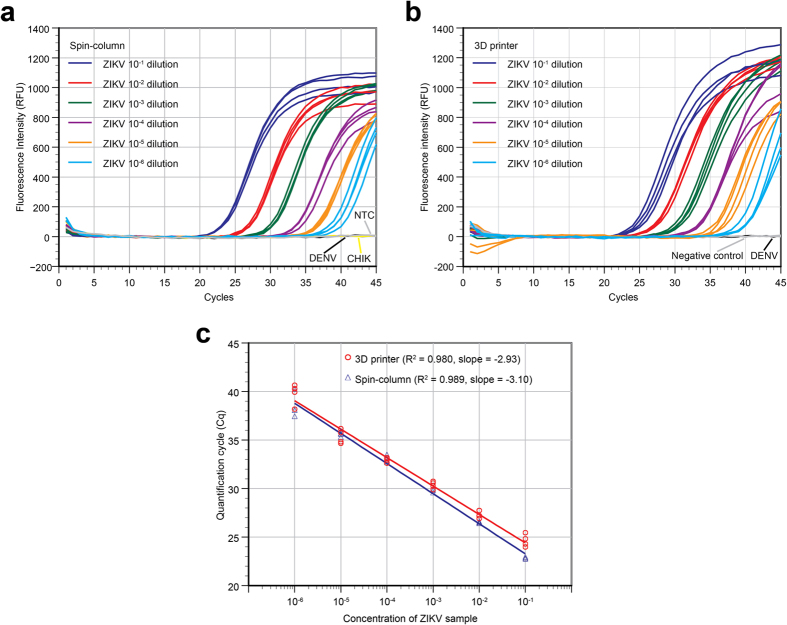
Figure 2. Real-time RT-PCR data from serially diluted ZIKV samples spiked in human urine.
(a) RNA templates were extracted from each concentration 4 times, using the spin-column protocol. Dengue viral RNA (DENV) and chikungunya viral RNA (CHIK) were used as negative controls of this real-time RT-PCR assay. NTC was the no-template control reaction. (b) RNA templates were extracted from each concentration 4 times, using the 3D printer protocol. Urine sample without ZIKV (Negative control), and dengue virus samples (DENV) were used as negative controls in the extraction process. (c) Standard curves were plotted from both the spin-column protocol and 3D printer protocol data. The R2 value and slope of the plot are included and the Qiagen spin-column extraction method appears to be slightly better with samples of higher concentrations (10−1 and 10−2 dilutions). Nevertheless, the results show that ZIKV concentrations as low as 10−6 can be effectively extracted by both methods and detected by a commercial thermal cycler using RT-PCR.