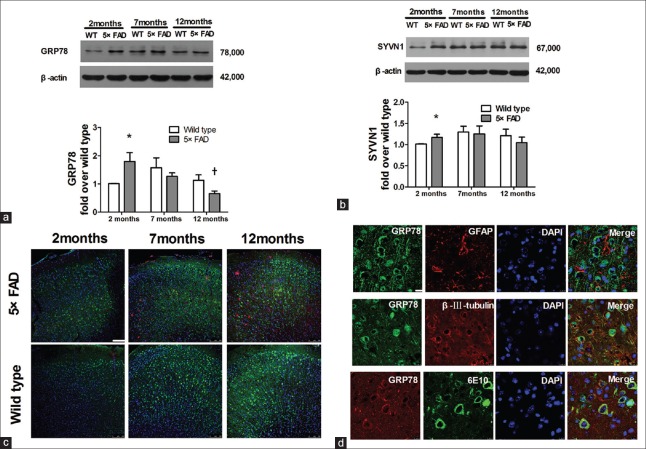
Figure 2.
Significant upregulation of anti-apoptotic factors, GRP 78 and SYVN1, in 2-month-old 5×FAD mice. (a) GRP 78 expression of 5×FAD mice and age-matched WT mice at 2, 7, and 12 months old (n = 6, *P < 0.05 vs. 2-month-old WT mice; †P < 0.01 vs. 2-month-old 5×FAD mice). (b) SYVN1 expression of 5×FAD mice and age-matched WT mice at 2, 7, and 12 months old (n = 5, *P < 0.05 vs. 2-month-old WT mice). (c) Confocal images of GRP 78 (green), 6E10 (Aβ, red) and nuclei (DAPI, blue) in the cortical slices of 2-, 7- and 12-month-old mice by immunofluorescence staining. Scale bar = 100 μm. (d) Confocal images of GRP 78 (green), GFAP (red) or β-III-tubulin (red) in the frontal cortical slices of 7-month-old 5×FAD mice by immunofluorescent staining. The bottom row of (d) indicates the immunofluorescent staining of GRP 78 (red) and 6E10 (green, targeting Aβ). Scale bar = 10 μm. 5×FAD: Transgenic mice with five familiar Alzheimer's disease; WT: Wild-type mice; GRP 78: Glucose-regulated protein 78; SYVN1: Ubiquitin ligase synovial apoptosis inhibitor 1; Aβ: Amyloid β; 6E10: The antibody targeting Aβ; GFAP: Glial fibrillary acidic protein; DAPI: 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.