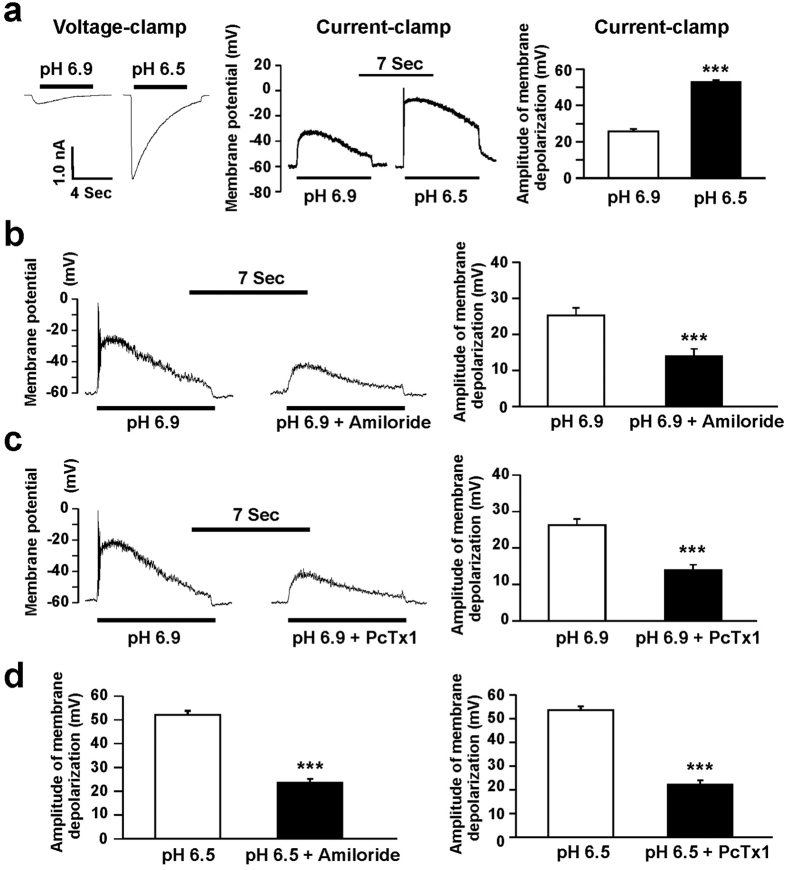
Figure 7. Activation of ASICs induces membrane depolarization in neurons from cultured mouse medullary neurons.
(a) Under voltage-clamp recording, ASIC currents were activated by a drop in pH from 7.4 to 6.9 or 6.5 in the same neuron (left panel). The ASIC currents were recorded in a total of 12 neurons. The pH 6.9 or 6.5 induced the membrane depolarization was recorded under current-clamp configuration in the same neuron (middle panel). The pH 6.5-induced membrane depolarization was much bigger than pH 6.9 (right panel). (b) and (c) Representative traces (left panel) and summary data (right panel) showing the membrane depolarization induced by a drop in pH from 7.4 to 6.9 was inhibited by amiloride (100 μM, n = 7, p < 0.001) and PcTx1 (10 nM, n = 8, p < 0.001), respectively. (d) Summary data showing the membrane depolarization induced by a drop in pH from 7.4 to 6.5 was inhibited by amiloride (100 μM, n = 5, p < 0.001, left panel) and PcTx1 (10 nM, n = 5, p < 0.001, right panel), respectively.