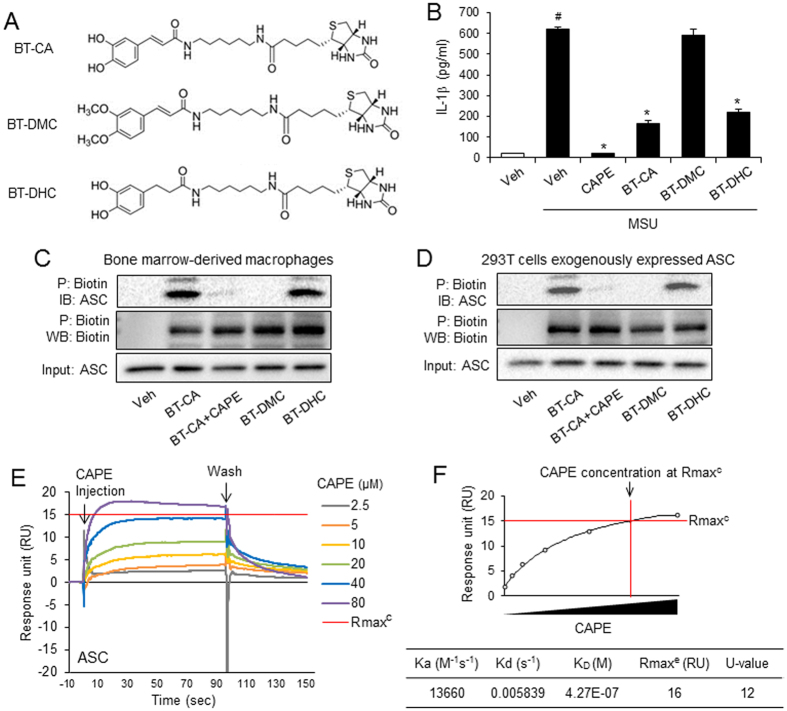
Figure 5. CAPE associated with ASC expressed endogenously and exogenously in the cell.
(A) The structure of biotin-tagged CA (BT-CA), biotin-tagged DMC (BT-DMC), and biotin-tagged DHC (BT-DHC). (B) LPS-primed BMDMs were treated with CAPE, BT-CA, BT-DMC, and BT-DHC (10 μM) for 1 hr and then stimulated with monosodium uric acid (MSU) crystals (500 μg/ml) for 6 hr. The cell culture supernatants were analyzed for secreted IL-1β using ELISA. The values represent the means ± SEM (n = 3). #Significantly different from vehicle alone, p < 0.0001. *Significantly different from MSU alone, p < 0.0001. (C) After BMDM cell lysates were treated with BT-CA, BT-DMC, and BT-DHC (1 μM) at room temperature for 4 hr, cell lysates were precipitated with NeutrAvidin beads and subjected to immunoblotting analysis. The amount of ASC expression in cell lysates were determined as “input”. CAPE (1 μM) was added to cell lysates treated with BT-CA. (D) After 293T cells were transfected with ASC-expression plasmids, the cell lysates were treated with BT-CA, BT-DMC, and BT-DHC (1 μM) at room temperature for 4 hr. The cell lysates were precipitated with NeutrAvidin beads and subjected to immunoblotting analysis. CAPE (1 μM) was added to cell lysates treated with BT-CA. (E) Sensograms of CAPE binding to recombinant ASC protein in the presence of detergent (0.005% Tween-20) were obtained from surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis. Different concentrations of CAPE are presented as an overlay plot aligned at the start of injection. (F) The line graph of dose-binding response unit curve and the table showing kinetic parameters of the binding between CAPE and ASC calculated using a simple 1:1 interaction model were from SPR analysis in (E). The maximal expected binding level (Rmaxc) was calculated by Biocore T200 evaluation software and Rmaxe value was obtained from experimental maximum response unit. Veh, vehicle. P, precipitation. IB, immunoblotting. WB, western blotting.