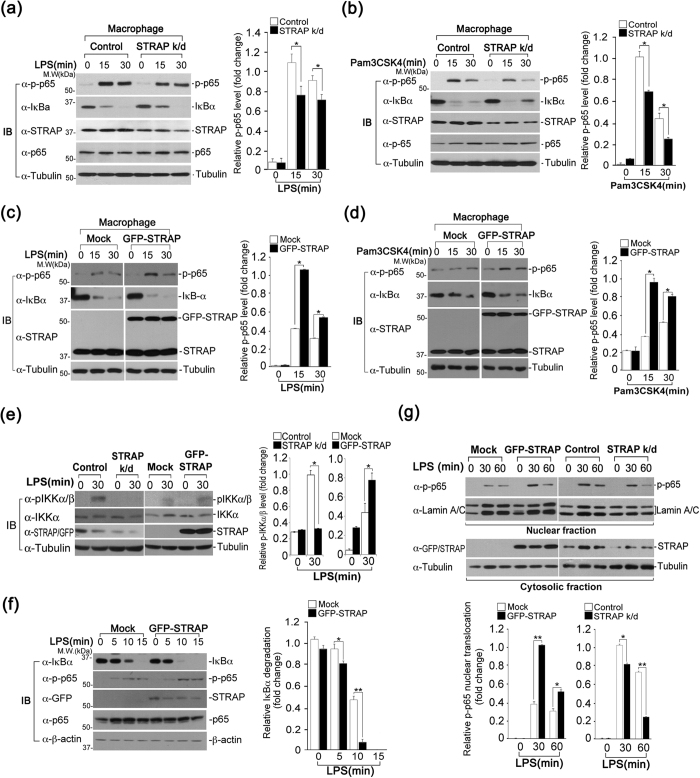
Figure 2. STRAP enhances phosphorylation of NF-κB p65.
(a–d) STRAP impacts the activation of p65. Phosphorylation of p65 was analyzed by immunoblotting in LPS-stimulated RAW macrophages stably expressing shRNA-GFP (control) or shRNA-STRAP (STRAP k/d) (a,b), and in mock-transfected or GFP-STRAP-expressing LPS-stimulated RAW macrophages (c,d). Expression levels of phosphorylated p65 were quantified by densitometry of bands and reported relative to tubulin. (e) The expression level of STRAP affects IKKα phosphorylation in response to LPS. Phospho-IKKα levels in STRAP-overexpressed or -depleted cells were determined by immunoblotting with anti-phospho-IKKα antibody. Expression levels of phosphorylated IKKα were quantified by densitometry of bands and reported relative to tubulin. (f) STRAP overexpression enhances a more rapid degradation of IκBα. The kinetics of IκBα degradation in STRAP-overexpressed or -depleted cells was determined by immunoblotting with anti-IκBα antibody. Expression levels of IκBα were quantified by densitometry of bands and reported relative to β-actin. (g) The nuclear translocation of phospho-p65 (p-p65) was influenced by STRAP expression levels. Expression of both STRAP and p-p65 was analyzed in the cytosolic and nuclear fractions of LPS-stimulated cells stably expressing GFP-STRAP or shRNA-STRAP (STRAP k/d) by immunoblotting. Tubulin and lamin A/C were used as loading controls for the cytosolic and nuclear fractions, respectively. Nuclear translocation levels of phosphorylated p65 were quantified by densitometry of bands and reported relative Lamin A/C. *P < 0.01 and **P < 0.005 (Student’s t-test). Data are representative of three independent experiments and are presented as mean ± s.d. in (a–g).