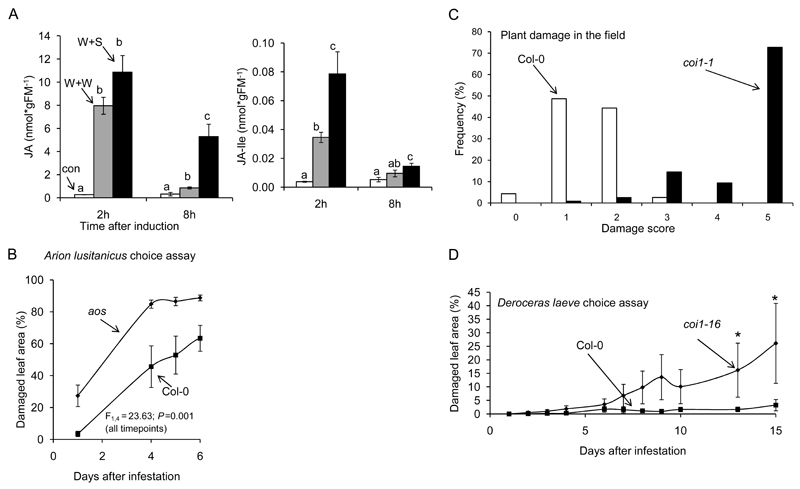
Figure 1. The jasmonate pathway defends Arabidopsis thaliana against slugs and snails.
(A) Wounded A. thaliana leaves treated with the mucus residue (“slime”) of crawling Arion lusitanicus (W+S) accumulate higher levels of jasmonic acid (JA) and its isoleucine conjugate (JA-Ile) when compared to wounded leaves treated with water (W+W) n ≥3, different letters indicate significant differences between treatments for each time point (ANOVA, Turkey HSD, P< 0.05). (B) Arion lusitanicus causes more damage on JA-deficient A. thaliana plants (AOC) when compared to WT (Col-0) (aos: 89 ±2%; Col-0: 63 ± 8%; ANOVA F1,4= 23,63; p= 0.008). (C) JA-perception deficient (coi1-1) A. thaliana plants suffer more damage by slugs than wild type (Col-0) plants in the field (Michigan, USA). Wilcoxon Test W = 13262, p < 2.2e-16. (D) The native slug Deroceras leave causes more damage on coi1-16 plants when compared to Col-0 in the lab (two way repeated measures ANOVA,*P<0.05).