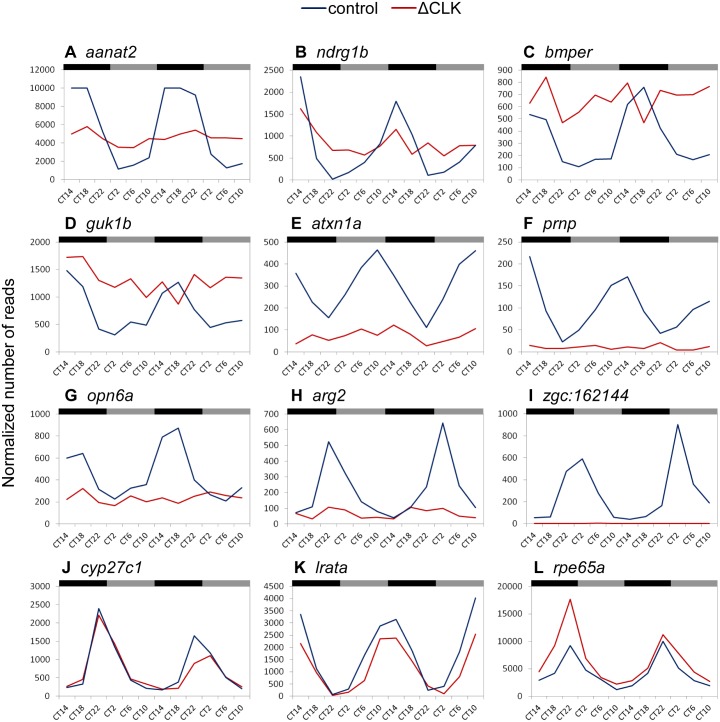
Fig 5. Diverse effects of ΔCLK on expression profiles of clock-controlled genes in the pineal gland.
Representative examples of expression profiles of CCGs in the pineal gland of control Tg(aanat2:EGFP) fish (control; blue trendline) compared with the expression profiles of these genes in the pineal gland of Tg(aanat2:EGFP-ΔCLK) fish (ΔCLK; red trendline). Black and gray bars denote subjective night and day, respectively. CT, circadian time. While the majority of CCGs became arrhythmic (A–I), a few maintained their circadian profile in the Tg(aanat2:EGFP-ΔCLK) pineal gland (J–L). For some of the CCGs that became arrhythmic in the Tg(aanat2:EGFP-ΔCLK) pineal gland the overall basal expression levels remained relatively intermediate or high (A–D), whereas for others the expression was down-regulated (E–H) or abolished (I).