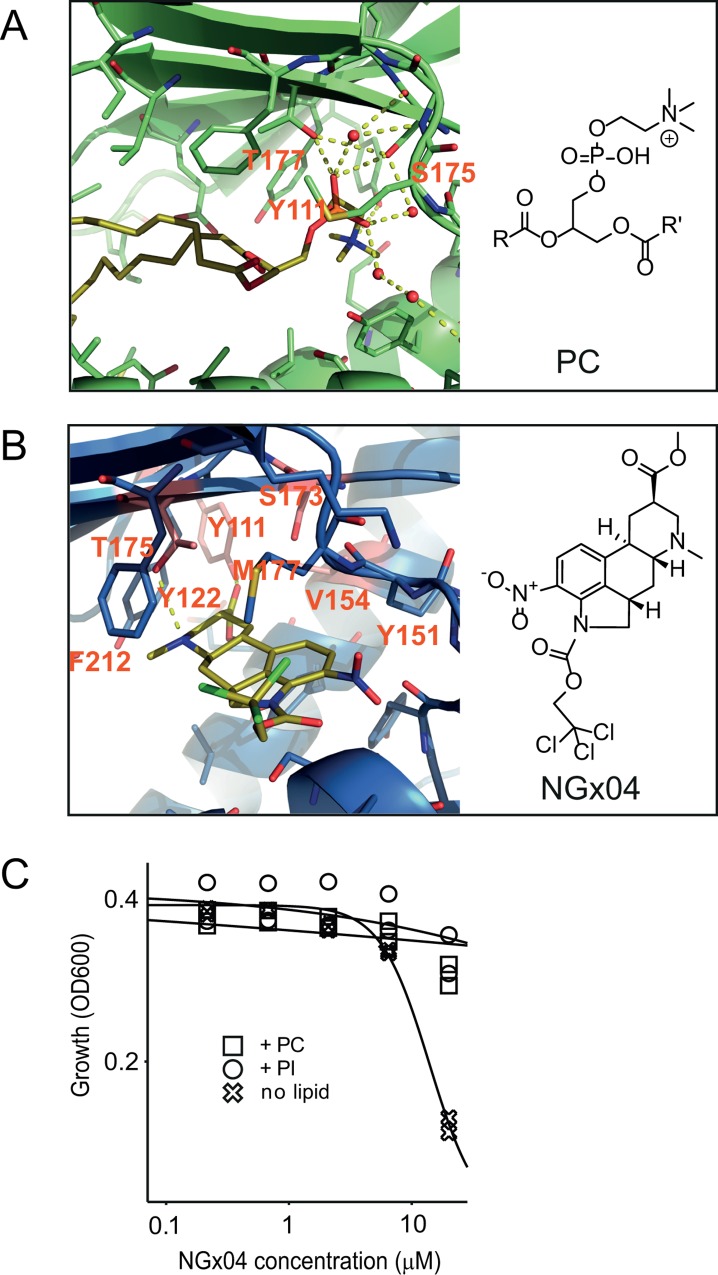
Fig 3. Active site antagonism.
Phosphatidylinositol (PI) and phosphatidylcholine (PC) competition. A) The crystal structure of Phosphatidylcholine (PC) bound to the yeast Sfh1protein (PDB ID: 3B7Q), (where R is oleoyl and R’ is palmitol). PC hydrophobic tail forms van der Waals interactions with a cluster of hydrophobic residue, whereas the phosphate moiety is interacting with the side-chain hydroxyl groups of residues S175 and T177, and the ethanolamine nitrogen contacts the phenolic oxygen of Y113. B) The proposed docking pose of NGx04 in the putative binding site of the yeast protein structure is shown (PDB ID:1AUA). In the suggested binding mode, the ester moiety of the ligand forms a hydrogen bond with Y111 while the ergoline amine forms H-bonds with the T175. The ergoline moiety is also forming van der Waals interactions with the following residues: Y122, Y151, S173, M177 and F212. C) Wild type yeast was grown in presence of increasing concentrations of NGx04, supplemented with either 200 μM PI, 200 μM PC or no phospholipid, incubated at 30°C and growth followed over time by measuring turbidity (OD600). Duplicate values were determined and the time points at 18 h were used for logistic regression.