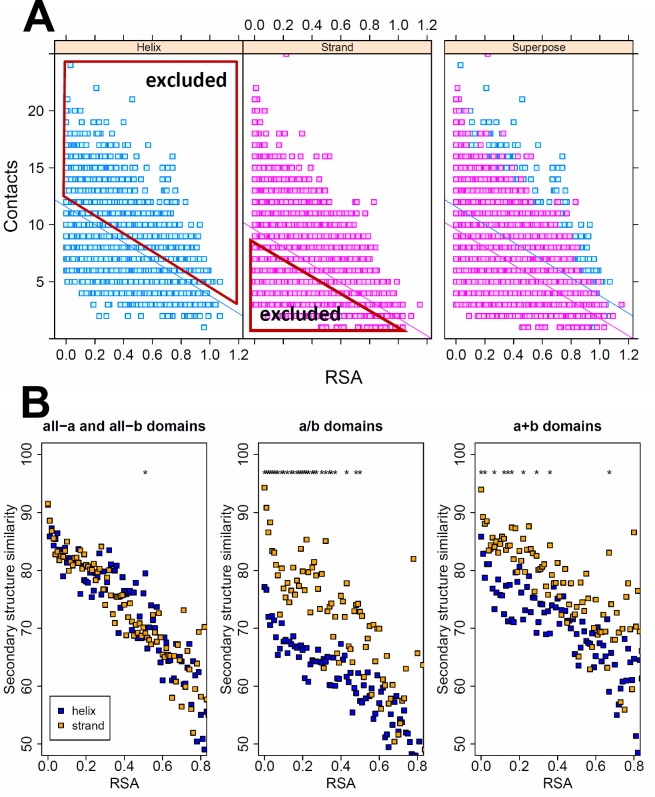
Fig 3. The effect of the number of residue contacts on secondary structure similarity.
A) Residues in helices have significantly more non-covalent interactions than residues in strands (ANCOVA using all-α and all-β domains). Using the two regression lines between RSA and the number of inter-residue contacts of each residue, we excluded all helix residues with higher than average number of contacts, and strand residues with lower than average number of contacts, and subsequently determined secondary structure similarity with the remaining residues. B) When using the remaining residue sets in all four SCOP classes, the difference in robustness between alpha helices and beta strands disappears, or even reverses (stars indicate significant difference, tests of proportions, p < 0.05 after Holm-Bonferroni correction), indicating that the higher robustness of helices is caused by their higher contact density.