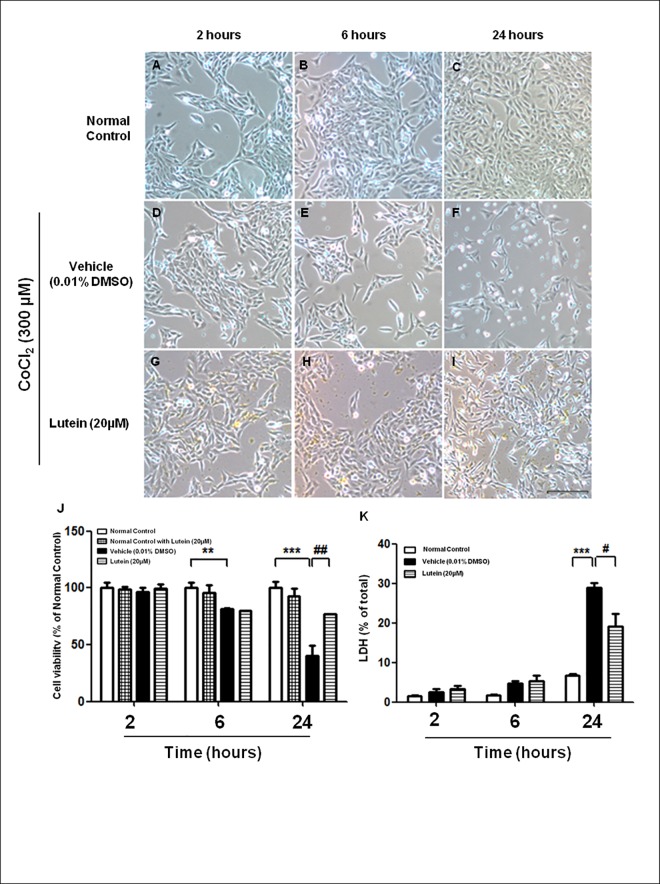
Fig 1. Lutein rescued rMC-1 cells from CoCl2-induced hypoxic injury.
rMC-1 cells were exposed to CoCl2 (300μM) with or without lutein for various periods. Representative photographs of rMC-1 cells (A-C) normal control, (D-F) hypoxia with vehicle (0.01% DMSO), (G-I) hypoxia with lutein (20μM). (J) Percentage of cell viability. Treatment of lutein only without hypoxia did not affect the viability when compared with the normal control. Lutein-treated rMC-1 cells showed higher cell viability when compared with the vehicle-treated group at 24 hours. (K) Percentage of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release from damaged cells. Lutein attenuated LDH release after CoCl2-induced injury when compared with that in vehicle-treated group at 24 hours. n = 5 in each group. **P< 0.01, ***P<0.001 versus normal control group; #P< 0.05, ##P<0.01 versus vehicle-treated group. Scale bar, 100 μm.