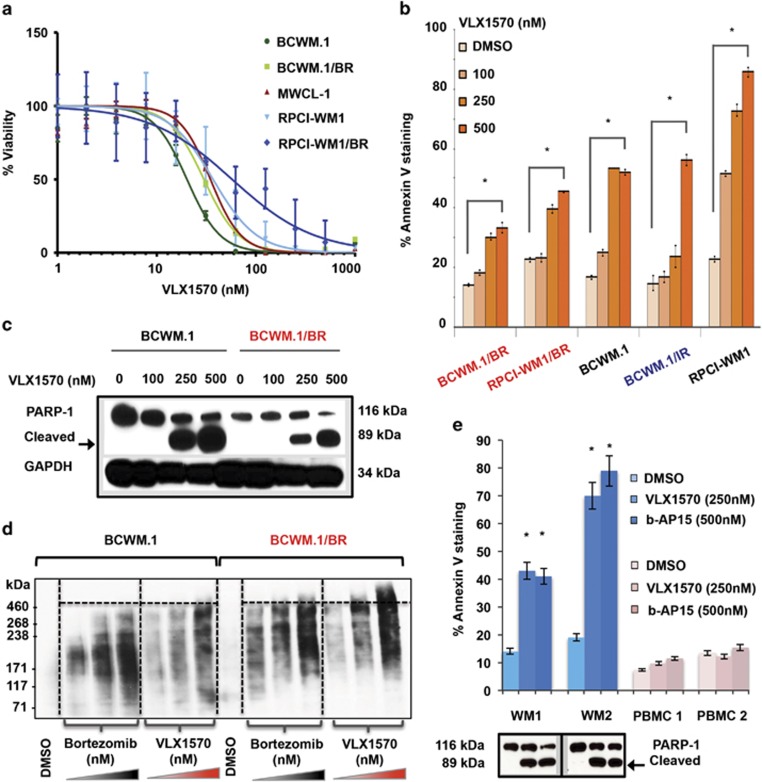
Figure 3.
VLX1570 induces loss of cell viability, apoptosis and accumulation of high-molecular-weight protein conjugates in drug-resistant WM cells. (a) Seventy-two hours MTS assay was conducted to assess sensitivity of WM cell lines (BCWM.1, MWCL-1 and RPCI-WM1) including their BR derivatives (BCWM.1/BR and RPCI-WM1/BR) towards VLX1570. Median EC50 (half-maximal effective concentration) of the cell lines tested was 29.96 nm (range, 20.2–93.59 nm). EC50 values for each individual cell lines are presented in Supplementary Table 1. (b) WM cell lines, including BR or IR subclones, were treated with DMSO or VLX1570 at indicated concentrations for 12 h and stained with Annexin-V and propidium iodide followed by flow cytometry to examine apoptosis. VLX1570 induced significant apoptosis (denoted by *) in all WM cell lines tested in a dose-dependent manner with (P=0.01–0.00003). The comparative percentage (and statistical significance) of % Annexin-V positivity in VLX1570-treated cell lines is presented in Supplementary Table 2. (c) Immunoblotting for poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) cleavage confirmed execution of apoptosis (representative BCWM.1 and its BR derivative, BCWM.1/BR shown). (d) Polyubiquitinated protein accumulation was examined in BCWM.1 and BCWM.1/BR cells after treatment with DMSO, bortezomib or VLX1570 at indicated concentrations for 3 h followed by isolation of protein lysates and immunoblotting with anti-polyubiquitin antibody. Notably, VLX1570 treatment in BCWM.1/BR cells resulted in higher-molecular-weight ubiquitinated protein buildup compared with bortezomib treatment. (e) Apoptosis in CD19+/CD138+ primary WM cells from two patients (WM1 and WM2) as well as PBMCs from healthy donors (PBMC 1 and PBMC 2) treated with either b-AP15 or VLX1570 at indicated concentrations for 12 h was examined as in (b). VLX1570 and b-AP15 induced nearly equivalent levels of significant apoptotic cell death in primary WM cells, whereas insignificant apoptosis was noted in PBMCs (relative to DMSO-treated cells). Apoptotic cell death in WM1 and WM2 cells was confirmed by immunoblotting for PARP-1 cleavage.