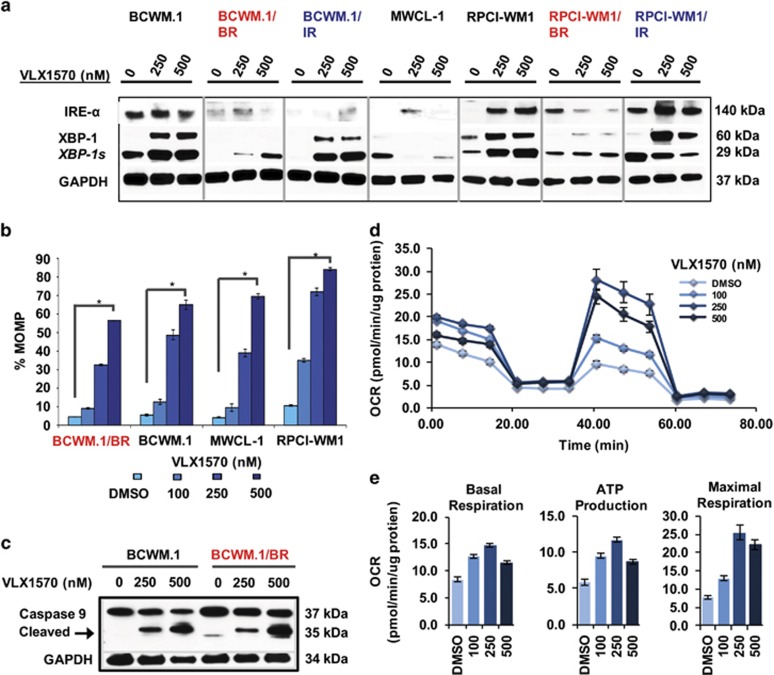
Figure 4.
VLX1570 invokes ER stress machinery and mitochondrial damage in WM cells. (a) WM cell lines including BR (red font) and IR subclones (blue font) were treated with VLX1570 at indicated concentrations for 12 h and subjected to immunoblotting with anti-IREα, anti-XBP-1, XPB-1 s and GAPDH antibodies. ER stress-associated protein XBP-1 (unspliced) as well as XBP1s (spliced) were markedly induced by VLX1570. (b) MOMP was measured in relation to TMRM fluorescence in all WM cell lines and TMRM-negative cells were calculated to represent (%) MOMP (four representative cell lines shown). MOMP was significantly induced in VLX1570-treated WM cells in a dose-dependent manner (denoted by *P=0.0000001–0.00025). (c) Immunoblot analysis demonstrated cleavage of caspase-9 after VLX1570 treatment (representative BCWM.1 and BCWM.1/BR shown). (d) Mitochondrial bioenergetics were measured at baseline in BCWM.1 cells followed by inhibition of the mitochondrial ATP production (introduction of oligomycin), uncoupling oxidative phosphorylation (OP) and ATP production causing maximal mitochondrial respiration (introduction of FCCP) and finally complete inhibition of the OP by combination of rotenone and antimycin A. Oxygen consumption rate (OCR) is displayed in values normalized to total protein content. VLX1570-treated cells (100, 250 and 500 nm) were analyzed side by side with DMSO-treated control cells. (e) Treatment of cells with VLX1570 caused concentration-dependent biphasic changes of all analyzed parameters: basal respiration (left), ATP production (middle) and maximal respiration (right); displaying maximal values in 250 nm concentration.