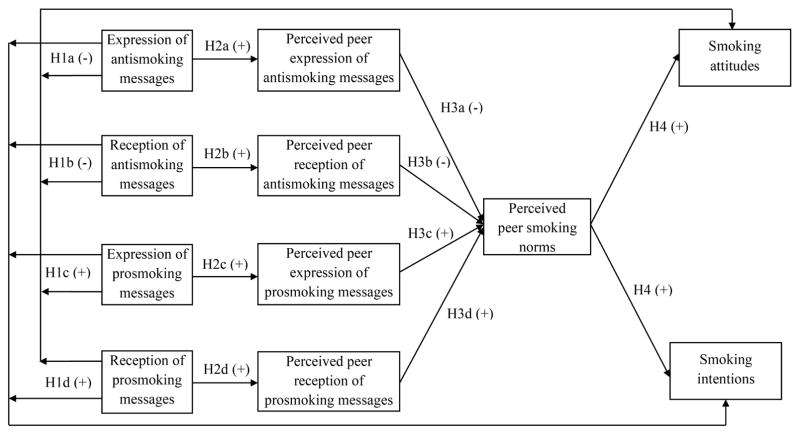
Fig. 1.
Hypothesized IPI model for examining the expression and reception effects of smoking-related social media messages on college students’ smoking. Note: Gender, ethnicity, family smoking, and family or friends with smoking-related illnesses are included as exogenous variables, but not shown here.