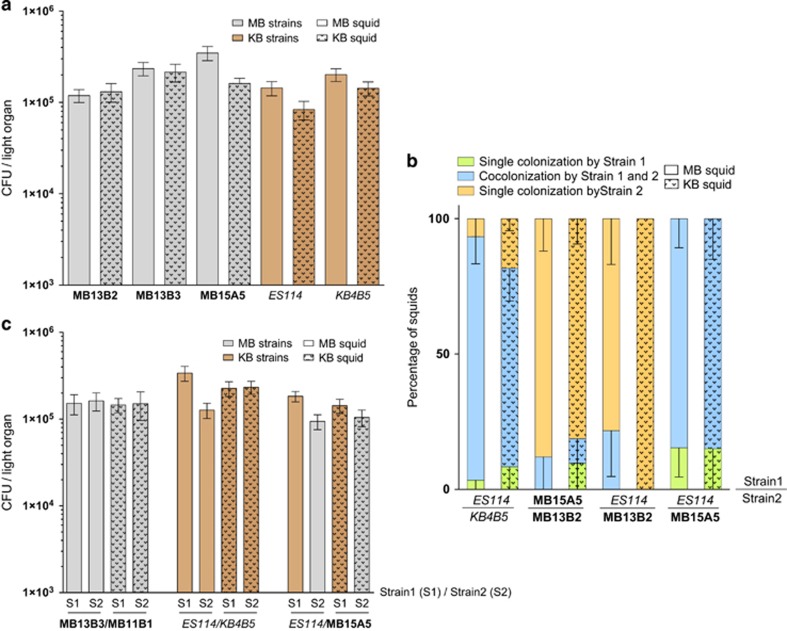
Figure 1.
Colonization of light organs of squids from either Maunalua Bay (MB; open bars) or KB (dotted bars) populations, by symbiont strains isolated from either MB (gray) or KB (brown) adult light organs. Inoculations were made with either single strains (a) or with pairs of strains (b and c). In all experiments, squid were incubated for 3 h with 103–104 CFU of bacteria per ml of FSIO, transferred to uninoculated FSIO and assayed after another 45 h for CFU per light organ. Values are means plus or minus the standard error of the mean (s.e.m.). (a) None of the values for the pairs of bars (open and dotted) were significantly different from each other. (b) Animals inoculated with pairs of strains were found to be co-colonized either by both strains (blue) or by only Strain 1 (green) or only Strain 2 (orange), and the percentage of the three classes are indicated by a fractionated bar graph. (c) In addition, when organs were analyzed that had been co-colonized by either two MB strains (MB11B1 and MB13B2), two KB strains (ES114 and KB4B5) or an MB and a KB strain (ES114 and MB15A5), the relative numbers of the two co-occurring strains were approximately equal in hosts from both populations, regardless of which population the strain had been originally isolated from.