Fig. 5. Implanted microcoils activate neuronal circuits in vivo.
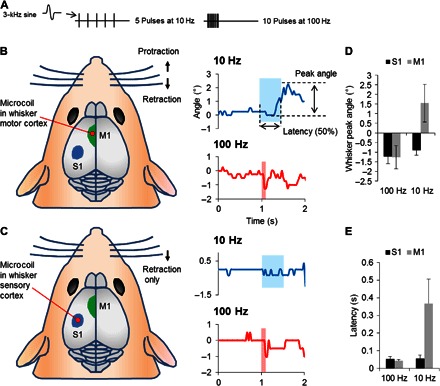
(A) Stimulus waveforms consisted of 5 pulses delivered at 10 Hz or 10 pulses delivered at 100 Hz. Each pulse consisted of one full period of a 3-kHz sinusoid with an amplitude of 112 mV. (B) Left: Coils were inserted into the whisker motor cortex (left hemisphere). Ten-hertz stimulation resulted in protraction of whiskers (upward deflections) on the right side (top), whereas 100-Hz stimulation induced retraction (downward deflections) (bottom). (C) Illustration of the approximate location for coil insertion to simulate the whisker sensory cortex. Both 10- and 100-Hz stimulation resulted in whisker retraction (top and bottom panels on the right). (D) Mean amplitudes of peak whisker movements for each stimulus condition. (E) Mean latency for the onset of whisker movements for each stimulus condition.
