Fig. 6. Continuous stimulation induces whisker movement at reduced power levels.
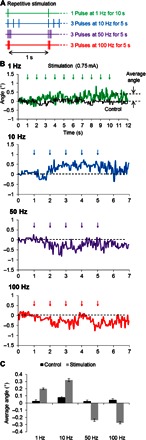
(A) Schematic illustration of the repetitive stimulation waveforms. Each “pulse” was a single 3-kHz sinusoid. (B) Averaged whisker movement in response to repetitive stimulation at power levels of 11.2 mV (0.75 mA). (C) Average whisker movements for each waveform (upward denotes protraction; downward indicates retraction).
