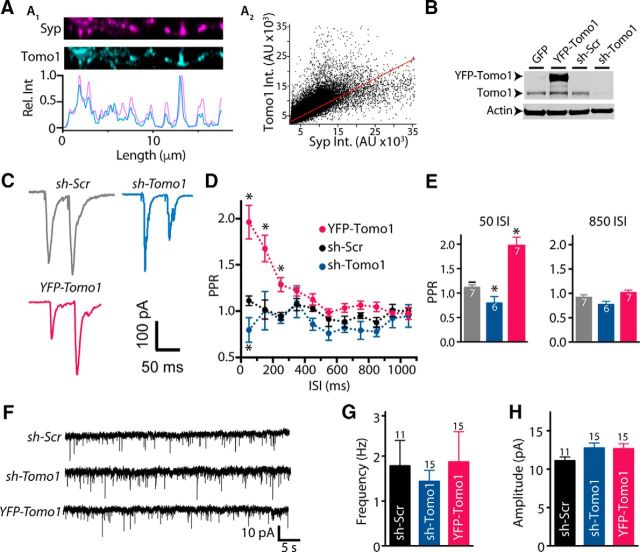
Figure 1.
Presynaptic localization of Tomo1 and inhibition of evoked neurotransmission in cultured hippocampal neurons. A1, Representative ICC images comparing endogenous Tomo1 with Syp, a presynaptic vesicular protein, within a straightened axon segment. Intensity line scans (A1, bottom) of axon segment show coincident immunofluorescent spikes of Tomo1 and Syp. A2, Fluorescence intensity relationship for spatially matched anti-Tomo1 and anti-Syp (Pearson r = 0.73, Mander's M1 = 0.8, M2 = 0.85 n = 29). B, Representative Western blot comparing Tomo1 immunoreactivity (anti-Tomo1) from lysate of lentiviral-infected GFP, YFP-Tomo1 (YFP-Tomo1), shRNA-Scramble (sh-Scr), or shRNA-Tomo1 (sh-Tomo1, top) hippocampal neurons. C, Representative paired-pulse stimulation EPSCs recorded from control (sh-Scramble), sh-Tomo1 KD, and YFP-Tomo1 OE lentiviral-infected conditions. PPRs to 50 ms ISI. D, Averaged PPR for all ISI values and (E) bar plots for the 50 ms and 850 ms ISI averages. F, Representative mEPSC records. G, Averaged mEPSC frequency and H, amplitude values (bottom) for lentiviral-infected neurons under control (sh-Scramble), sh-Tomo1 KD, and YFP-Tomo1 OE conditions. No significant differences were found in frequency or amplitude of spontaneous mEPSC between conditions. In this and all subsequent figures, graphs represent mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05.