Figure 3.
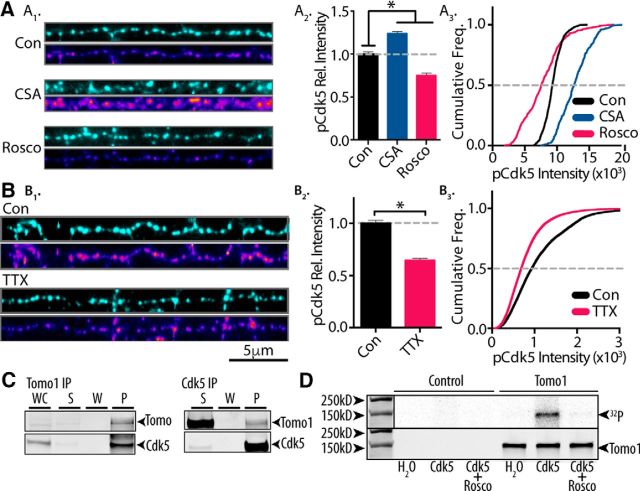
Tomo1 serves as catalytic substrate for neural activity-sensitive Cdk5. A1, Representative immunofluorescent images of Synapsin 1 (cyan, top) and phosphorylated Cdk5 (pCdk5; heat scale, bottom) in straightened axon segments from neurons treated (30 min) with CSA (50 μm), Rosco (100 μm), or control (DMSO, 0.5%). A2, Averaged pCdk5 immunofluorescence intensity relative to vehicle control. A3, Cumulative frequency of pCdk5 intensity across boutons shows that inhibition of Cdk5 by Rosco significantly reduces pCdk5 immunoreactivity, whereas CSA treatment enhances pCdk5 relative to control. B1–B3, pCdk5 immunofluorescence images comparing chronic silencing of neural activity by TTX (24 h, 1 μm) with control. Averaged pCdk5 intensity (B2) and cumulative frequency of pCdk5 (B3) intensity demonstrate that chronic dampening of neural activity significantly reduces Cdk5 activation. A, B, Analysis was performed on 45 images/preparation per condition and repeated on 3 neuronal preparations. C, Immunoblots showing coprecipitation of Tomo1 and Cdk5 from cultured hippocampal neuron lysates regardless of primary target of IP (Tomo1 or Cdk5). D, In vitro phosphorylation of affinity-purified Tomo1 by Cdk5/p25 as measured by 32P labeling. 32P-radioactive signal (top) and anti-Tomo1 immunoreactivity (bottom) on Western blot corresponding to the following conditions: absence of Cdk5/p25 kinase (H2O), Cdk5/p25 kinase (Cdk5), and Cdk5/p25 + 1 mm Rosco (Cdk5 + Rosco). *p < 0.05.