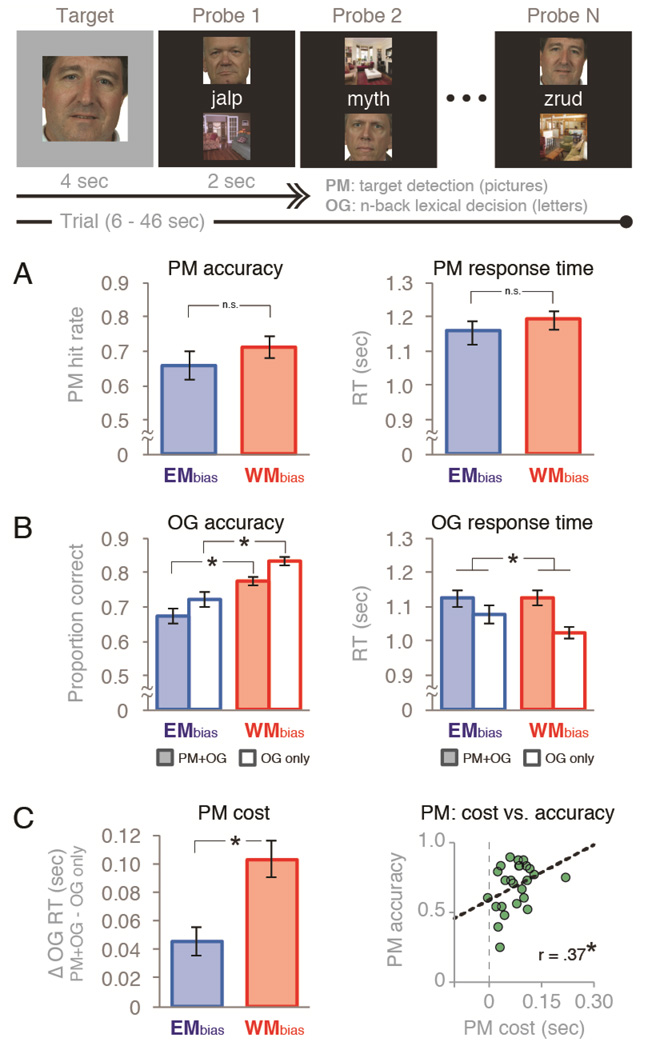
Figure 1.
Task diagram and behavioral performance. The dual-task experiment consisted a picture-target detection prospective memory task (“PM”) embedded in an ongoing lexical-decision task (“OG”). Half of the trials were WMbias trials (1-back lexical decisions and a small set of repeating homogeneous pictures) and half were EMbias trials (2-back lexical decisions and a large set of trial-unique heterogeneous pictures). Two-thirds of all trials included both tasks (“PM+OG”), and one-third did not require PM responses (“OG only”) Behavioral performance on (A) the PM task in PM+OG trials and (B) the OG task in all trial conditions. (C) Dual-task costs on reaction time in the OG task due to the addition of the PM task (“PM cost”) , and its relationship to PM accuracy across participants. Error bars indicate s.e.m.,*p < .05.