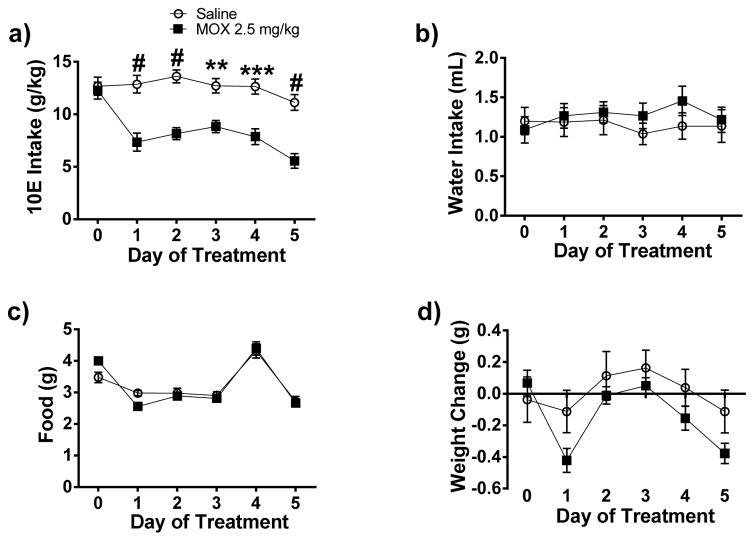
Figure 3. Daily administration of MOX (2.5 mg/kg x 5 days) significantly reduced 10E intake in female C57BL/6J mice using a 24-h-two-bottle choice paradigm.
Following habituation with saline injection and attaining stable drinking levels, MOX was administered for 5 consecutive days. Squares represent MOX and circles represent saline. a) MOX (2.5 mg/kg) significantly reduced 10E intake across the 5 treatment days. The effects of water intake, food intake, and weight are presented in panels, b, c, and d, respectively. Values represent mean ± SEM cumulative intake for MOX (18 mice) and saline (10 mice), ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, # p < 0.0001 versus saline-treated group, Bonferroni’s post-hoc test.