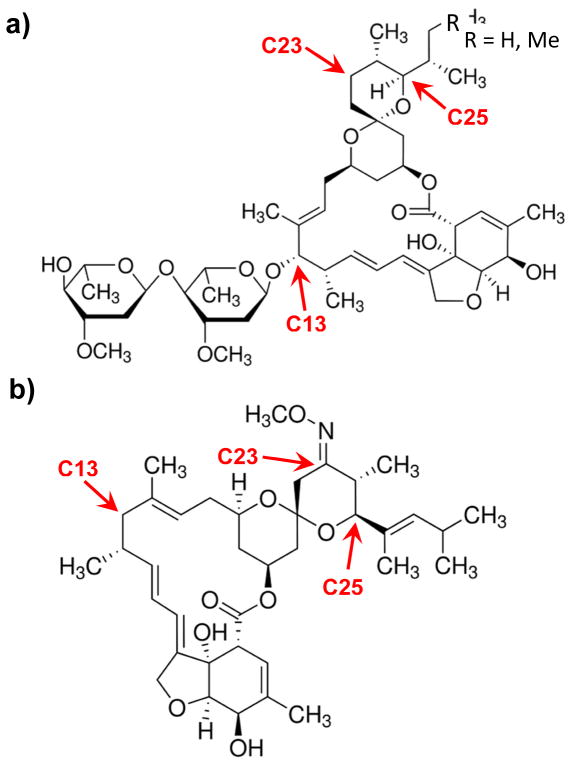
Figure 7. Structures of (a) ivermectin and (b) MOX.
Major structural differences are noted. C13: ivermectin contains a disaccharide while MOX is protonated; C23: MOX has a methoxime; C25: ivermectin is a mixture of C25-ethyl (~10%) or C25-methyl (~90%) groups while MOX has a dimethyl-butyl substituent.