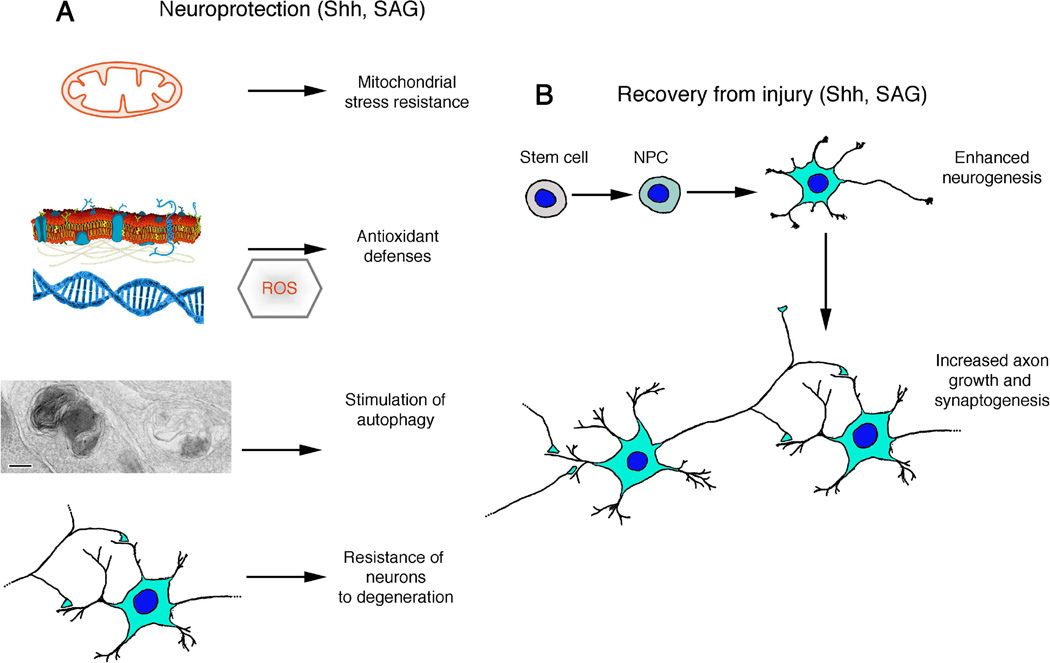
Figure 3. Potential applications of Shh pathway agonists in the treatment of nervous system injury and neurological disorders.
(A) Shh signaling may protect neurons against dysfunction and degeneration by engaging multiple pathways that bolster the resistance of neurons to excitotoxic, metabolic and proteotoxic stress. Among the neuroprotective mechanisms of action of Shh are enhancement of mitochondrial stress resistance and antioxidant defenses and stimulation of autophagy. Two different autophagosomes are shown in a presynaptic terminal from a hippocampal neuron culture treated with Shh (scale bar is 100 nm; modified from Fig. 3E in [75]). Cell membrane and DNA drawings are public domain images. (B) Shh signaling can enhance recovery of function following a traumatic or ischemic injury to the nervous system by stimulating neurogenesis, axon growth and synaptogenesis. NPC, neural progenitor cell; ROS, reactive oxygen species.