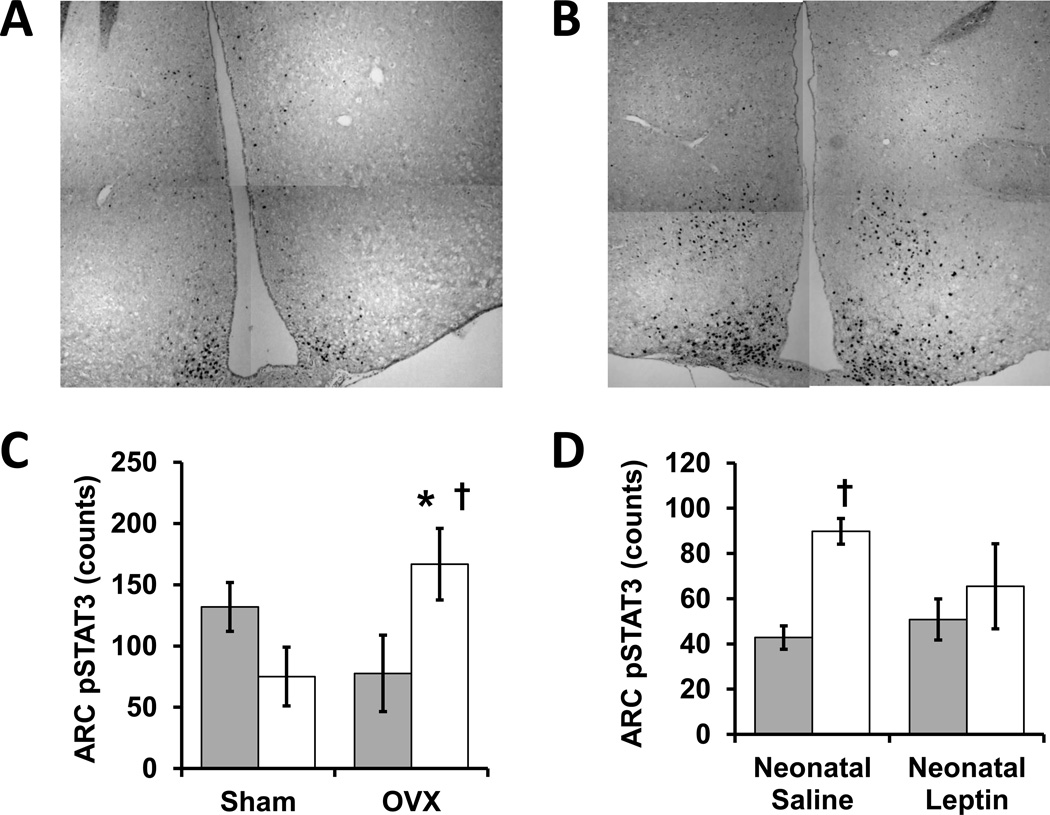
Figure 2.
The influence of perinatal growth, ovarian status and neonatal leptin administration on leptin-stimulated hypothalamic signaling in adult mice. These original experiments with C57BL/6J mice (Jackson Laboratory) were approved by the University of Iowa Office of Animal Resources. Neonatal growth restriction (GR) was induced by placing mice into litters of 12 rather than 6 pups on postnatal day 1, and GR was confirmed by weanling weights below the 10th percentile for the colony on postnatal day 20. At 2 to 4 months, female mice underwent bilateral ovariectomy (OVX) or sham surgery (incisions without ovary removal) under inhaled isoflurane anesthesia (4%, Phoenix Scientific). After 2 to 3 months of postoperative recovery, a 3 hour fast was followed by intraperitoneal injection of murine leptin (1 mg/kg, Biomyx Technology) one hour prior to transcardiac perfusion fixation during anesthesia with intraperitoneal ketamine (262.5 mg/kg, Sigma-Aldrich) and xylazine (37.5 mg/kg, Sigma-Aldrich). Coronal cryosections were obtained though the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus (ARC) and pSTAT3 immunoreactivity was quantified with anti-phospho-STAT3 (9145, Cell Signaling) followed by detection with ImmPRESS/DAB (MP-7401, Vector Laboratories). Representative immunostains (A, Control-OVX; B, GR-OVX) are composites of 4 higher magnification images. C, Leptin-stimulated pSTAT3-positive cells counts were influenced by a significant interaction between GR and adult ovarian status (control: closed bars, GR: open bars, N = 4 or 5). OVX significantly increased leptin-evoked pSTAT3 signaling in GR mice (†P<0.05 by ANOVA) such that GR-OVX mice had significantly more pSTAT3 reactive nuclei than control-OVX mice (*P<0.05 by ANOVA), suggesting adult ovarian function suppresses GR-associated leptin responsiveness. Compared to control-OVX mice, GR-OVX mice also tended to have more pSTAT3 reactive nuclei in the ventral medial hypothalamus, but the difference did not reach statistical significance (control-OVX 11+/−6, GR-OVX 31+/−7). D, Unlike the significant increase in ARC pSTAT3 seen in control (neonatal saline) mice that received leptin (open bars) versus saline (closed bars) prior to perfusion fixation (†P<0.05 by ANOVA), neonatal leptin-treated mice did not have significantly different responses to pre-fixation injection of leptin versus saline, suggesting neonatal leptin administration decreased adult leptin responsiveness (N= 3 or 4).