Figure 10. Human PBGS F12L compared to wild type (N59 allele)8.
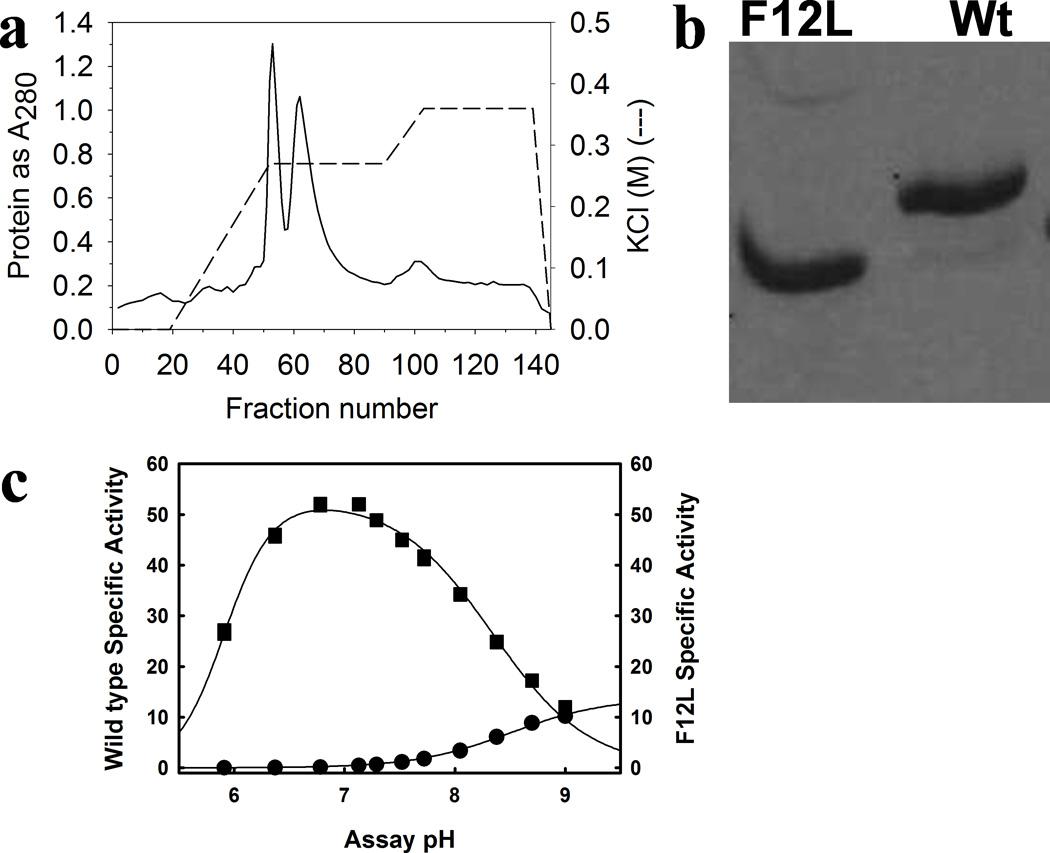
(a) The anion exchange separation of PBGS hexamer (early eluting peak, exemplified by F12L) and the PBGS octamer (later eluting peak, as exemplified by the wild type allele N59). (b) Native PAGE (Phastgel) behavior of purified F12L, shown by crystallography to be a hexamer, and wild-type human PBGS, shown by crystal structure to be an octamer. (c) The pH activity profile for wild type human PBGS (squares) vs. the F12L variant (circles), at 10 mM ALA, in 0.1 M bis-tris propane. Later work9 established that at pH 9, wild type human PBGS is predominantly hexamer.
